724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Page 82
LGB5028A User‘s Manual
724-746-5500 | blackbox.com
Chapter 6: Configuration
The switch will use the last entry of the currently displayed table as a basis for the next lookup. When the end is reached, the text
“No more entries” is shown in the displayed table. Use the button to start over.
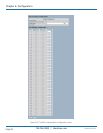
IGMPv3 Information Table Columns
VLAN ID: VLAN ID of the group.
Group: Group address of the group displayed.
Port No.: Switch port number.
Mode: Indicates the filtering mode maintained per (VLAN ID, port number, Group Address) basis. It can be either “Include” or
“Exclude.”
Source Address: Show the IP Address of the source. Currently, system limits the total number of IP source addresses for filtering
to 128.
Type: Indicate the Type. It can be either “Allow” or “Deny.”
Auto-refresh: Check the button and the device will refresh the log automatically.
Upper right icon (Refresh, <<, >> ): Click the “Refresh” button to refresh the device automatically. Use the “<<” and “>>”
buttons to go to the next/previous page or entry.
6.6 MLD Snooping
A network node that acts as a source of IPv6 multicast traffic is only an indirect participant in MLD snooping—it just provides
multicast traffic, and MLD doesn’t interact with it.
NOTE: In an application such as desktop conferencing, a network node may act as both a source and an MLD host; but MLD
interacts with that node only in its role as an MLD host.
A source node creates multicast traffic by sending packets to a multicast address. In IPv6, addresses with the first eight bits set
(that is, “FF” as the first two characters of the address) are multicast addresses, and any node that listens to such an address will
receive the traffic sent to that address. Application software running on the source and destination systems cooperates to
determine what multicast address to use.
NOTE: This is a function of the application software, not of MLD.
When MLD snooping is enabled on a VLAN, the switch acts to minimize unnecessary multicast traffic. If the switch receives
multicast traffic destined for a given multicast address, it forwards that traffic only to ports on the VLAN that have MLD hosts for
that address. It drops that traffic for ports on the VLAN that have no MLD hosts.