Technical Reference Guide
6.2.3 POWER MANAGEMENT
These systems include power management functions designed to conserve energy. These
functions are provided by a combination of hardware, firmware (BIOS) and software. The system
provides the following power management features:
J
Intel Pentium III processor with SpeedStep technology
J
ACPI v1.0b compliant (ACPI modes C1, C2, S1, and S3, )
J
API 1.2 compliant
J
U.S. EPA Energy Star compliant
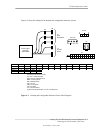
Table 6-1 shows the comparison in power states.
Table 6-1. System Power States
Table 6-1.
System Power States
Power
State
System Condition
Power
Consumption
Transition
To S [2] 0 by
OS Restart
Required
G0, S0, D0 System fully on. OS and application
is running, all components.
Maximum N/A No
G1, S1, C1, D1 System on, CPU is executing and
data is held in memory. Some
peripheral subsystems may be on
low power. Monitor is blanked.
Low < 2 sec after
keyboard or
pointing device
action
No
G1, S2/3, C2,
by/ D2 (Stand
suspend)
System on, CPU not executing,
cache data lost. Memory is holding
data, display and I/O subsystems on
low power.
Low < 5 sec. after
keyboard,
pointing device,
or power button
action
No
G1, S4, D3
(Hibernation)
d to disk for
Low
pow on
action
Yes
System off. CPU, memory, and
most subsystems shut down.
Memory image save
recall on power up.
<25 sec. after
er butt
System off. All components either
completely shut down or receiving
minimum po
wake-up.
<35 sec. after
er butt
System off (mechanical). No power
to any internal c
RTC circuit. [1]
G2, S5, D3
cold
wer to perform system
Minimum
pow on
action
Yes
G3
omponents except
None — —
NOTES:
Gn = Global state.
Sn = Sleep state.
Cn = ACPI state.
] Actual transition time dependent on OS and/or application software.
Dn = PCI state.
[1] Power cord is disconnected for this condition.
[2
Compaq Evo and Workstation Personal Computers
Featuring the Intel Pentium 4 Processor
Second Edition - January 2003
6-5