Chapter 2 System Overview
2.4.1 INTEL PENTIUM 4 PROCESSOR
The models covered in this guide feature the Intel Pentium 4 processor. This processor is
backward-compatible with software written for the Pentium III, Pentium II, Pentium MMX,
Pentium Pro, Pentium, and x86 microprocessors. The processor architecture includes a floating-
point unit, 32-KB first and 512-KB secondary caches, and enhanced performance for multimedia
applications through the use of multimedia extension (MMX) instructions. Also included are
streaming SIMD extensions (SSE and SSE2) for enhancing 3D graphics and speech processing
performance. The Pentium 4 processor features Net-Burst Architecture that uses hyper-pipelined
technology and a rapid-execution engine that runs at twice the processor's core speed.
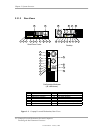
These systems employ an mPGA478B zero-insertion-force (ZIF) socket designed for mounting a
“Flip-Chip” (FC-PGA2) processor package (Figure 2-10). Small form factor units use a passive
heat sink held in place over the FC-PGA package with two retaining clips. Desktop and
configurable minitower units use an active assembly (which integrates the heat sink and fan) that
clips on to the processor socket over the FC-PGA package.
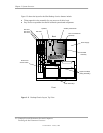
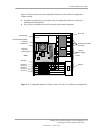
Figure 2–10. Processor Assembly And Mounting
FC-PGA2 Package
(w/ Integrated Heat
Spreader)
mPGA478B
Socket
Lock/Unlock
Handle
(Shown in unlock position)
Heat Sink
Retaining Clips
Heat Sink for
Small Form Factor Units
Heat Sink / Fan Assembly for
Desktop and
Configurable Minitower Units
These systems support processors fitted with passive heat sinks or processors fitted with heat
sink/fan assembly with a power cable that attaches to a fan-power header provided on the system
board. There are three types of passive heat sinks.
NOTE: The two types of heat sinks are not interchangeable. Also, these systems support
processors using the FC-PGA2 package only.
Compaq Evo and Workstation Personal Computers
Featuring the Intel Pentium 4 Processor
Second Edition – January 2003
2-14