Appendix G
116 E-Class DPL Programmer’s Manual
W1c / W1C: DataMatrix
Valid Characters: Any eight-bit byte data
Variable Length (W1c): This is a two-dimensional matrix symbology comprised of square modules
arranged within a perimeter finder pattern. Two types are ECC 000 – 140 and ECC 200.
Specified Length (W1C): Same as the variable length, however, with a Byte Count Specifier values
0x00 through 0xFF can be used within the data string without conflicting with the DPL format record
terminators.
ECC 000 – 140 symbols: These square symbols can be any odd sizes from 9x9 to 49x49, which may
be specified in the fields kkk and lll. If the symbol is specified with even numbers of rows or
columns, the next largest odd value will be used. Input values greater than 49 or less than 9 will
cause the symbol to be automatically sized for the input character stream. The record structure is
expanded for visual clarity.
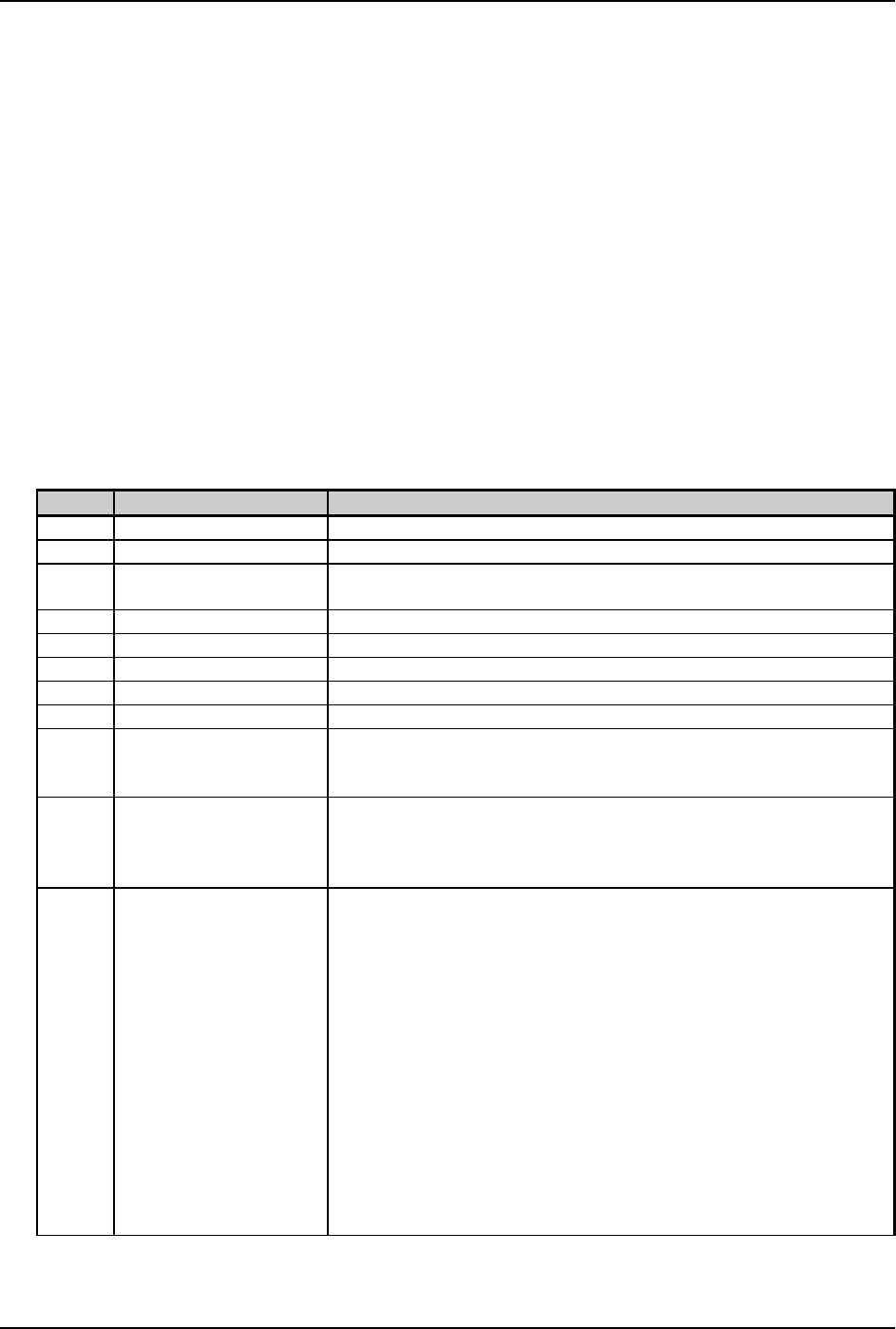
Record Structure: a W1 b c d eee ffff gggg [hhhh] iii j kkk lll mm…m
Where:
Field Valid Inputs Meaning
a
1,2,3, and 4 Rotation
W1
W1 Fixed value, extended barcode set
b
candC Lowercase selects the DataMatrix bar code, variable length
Uppercase selects the Datamatrix barcode with a Byte Count Specifier
c
1–9andA–O Module size horizontal multiplier
d
1–9andA–O Module size vertical multiplier
eee
000 – 999 No effect; must be numeric
ffff
0000 – 9999 Label position, row
gggg
0000 – 9999 Label position, column (see Appendix J)
[hhhh]
0000 to 9999 Optional string length specifier. Field termination is set by this byte
count. This decimal value includes all of the data following this byte
count field, but does not include itself.
iii
000, 050, 080, 100, 140 3-digit convolutional error correction level.
If any number other than one of these options is entered then the nearest
lesser value from the valid entries is used (e.g., selecting a value of 099
will cause an actual ECC value of 080 to be used).
j
0–6 Format identification, where:
0 - Automatically selects an encodation scheme based on the
characters to be encoded.
1 - Numeric data.
2 - Upper case alphabetic.
3 - Upper case alphanumeric and punctuation characters (period,
comma, hyphen, and slash).
4 - Upper case alphanumeric.
5 - ASCII, the full ASCII character set.
6 - Any 8-bit byte.
If a format identifier is selected which will not encode the input
character stream then the barcode symbol will not be printed. It is
recommended that the auto-encodation format identification be used
since it will select the best possible encoding scheme for the input
stream.


















