Chapter 3 Troubleshooting 3-27
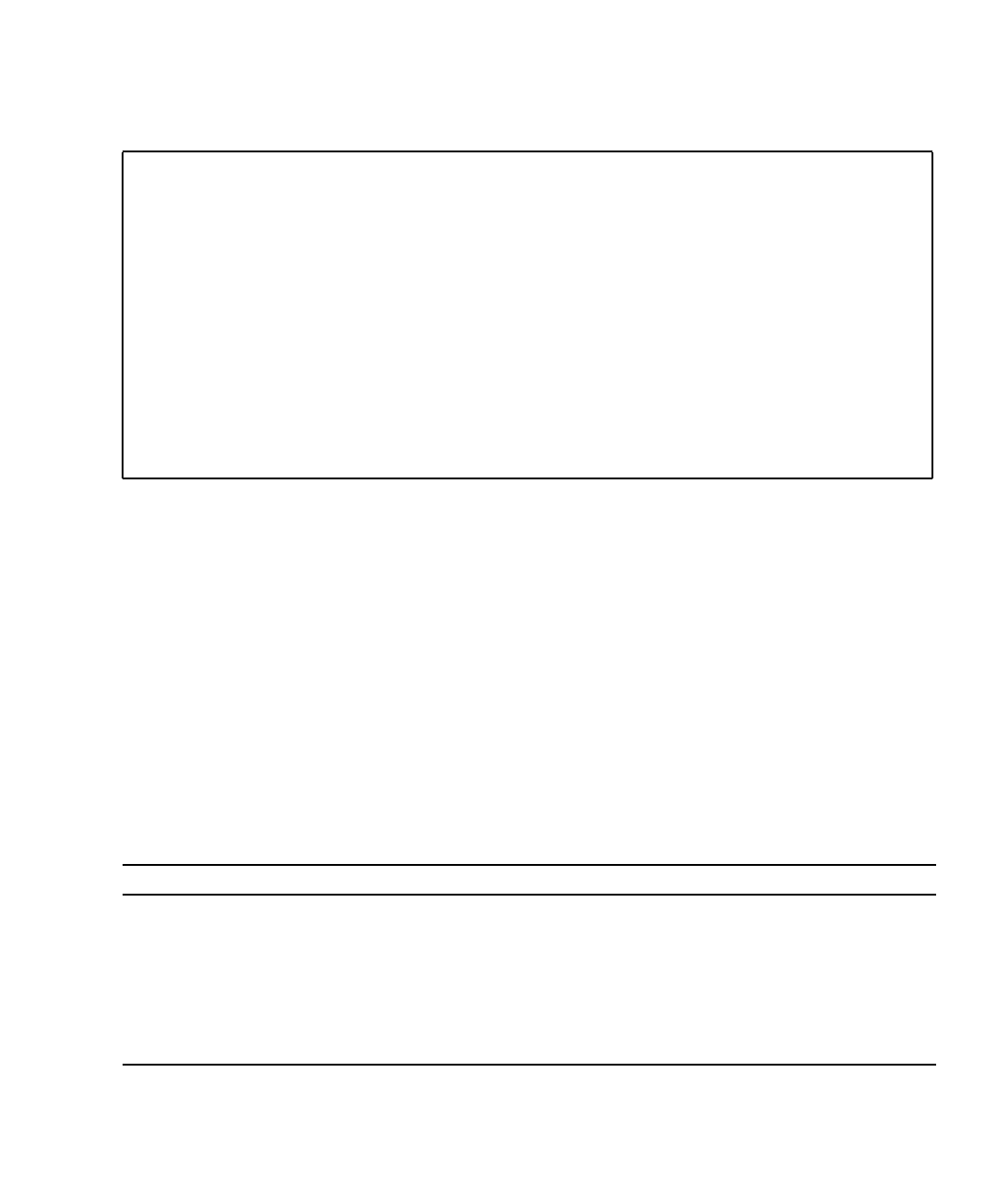
The following example shows the output for the netstat -p command:
3.6.5 Using the ping Command
The ping command sends an ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packet to a network host.
Depending on how the ping command is configured, troublesome network links or
nodes can be identified from the displayed output. The destination host is specified
in the variable hostname.
3.6.5.1 Options
TABLE 3-11 lists the options of the ping command and how those options can help
troubleshooting.
# netstat -p
Net to Media Table: IPv4
Device IP Address Mask Flags Phys Addr
------ -------------------- --------------- -------- ---------------
bge0 san-ff1-14-a 255.255.255.255 o 00:14:4f:3a:93:61
bge0 san-ff2-40-a 255.255.255.255 o 00:14:4f:3a:93:85
sppp0 224.0.0.22 255.255.255.255
bge0 san-ff2-42-a 255.255.255.255 o 00:14:4f:3a:93:af
bge0 san09-lab-r01-66 255.255.255.255 o 00:e0:52:ec:1a:00
sppp0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255
bge0 san-ff2-9-b 255.255.255.255 o 00:03:ba:dc:af:2a
bge0 bizzaro 255.255.255.255 o 00:03:ba:11:b3:c1
bge0 san-ff2-9-a 255.255.255.255 o 00:03:ba:dc:af:29
bge0 racerx-b 255.255.255.255 o 00:0b:5d:dc:08:b0
bge0 224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 SM 01:00:5e:00:00:00
#
TABLE 3-11 Options for ping
Option Description How it can help
hostname The probe packet is sent to hostname and
returned.
Verifies that a host is active on the network.
-g hostname Forcibly routes the probe packet through a
specified gateway.
By sending the probe packet through different
routes to the target host, individual routes can
be tested for quality.
-i interface Specifies through which interface to send and
receive the probe packet.
Enables a simple check of secondary network
interfaces.


















