Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families 155
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Electrical Specifications
7.9.5 Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance
Overshoot (or undershoot) is the absolute value of the maximum voltage above or
below V
SS,
see Figure 7-9. The overshoot/undershoot specifications limit transitions
beyond V
CCD
or V
SS
due to the fast signal edge rates. The processor can be damaged
by single and/or repeated overshoot or undershoot events on any input, output, or I/O
buffer if the charge is large enough (that is, if the over/undershoot is great enough).
Determining the impact of an overshoot/undershoot condition requires knowledge of
the magnitude, the pulse direction, and the activity factor (AF). Permanent damage to
the processor is the likely result of excessive overshoot/undershoot.
Baseboard designs which meet signal integrity and timing requirements and which do
not exceed the maximum overshoot or undershoot limits listed in Table 7-23 will insure
reliable IO performance for the lifetime of the processor.
Notes:
1. These specifications are measured at the processor pad.
2. Refer to Figure 7-9 for description of allowable Overshoot/Undershoot magnitude and duration.
3. TCH is the minimum high pulse width duration.
4. For PWRGOOD DC specifications see Table 7-21.
7.9.5.1 Overshoot/Undershoot Magnitude
Overshoot/Undershoot magnitude describes the maximum potential difference between
a signal and its voltage reference level. For the processor, both overshoot and
undershoot magnitude are referenced to V
SS
. It is important to note that the overshoot
and undershoot conditions are separate and their impact must be determined
independently.
The pulse magnitude and duration, and activity factor must be used to determine if the
overshoot/undershoot pulse is within specifications.
7.9.5.2 Overshoot/Undershoot Pulse Duration
Overshoot/undershoot pulse duration describes the total amount of time that an
overshoot/undershoot event exceeds the overshoot/undershoot reference voltage. The
total time could encompass several oscillations above the reference voltage. Multiple
overshoot/undershoot pulses within a single overshoot/undershoot event may need to
be measured to determine the total pulse duration.
Note: Oscillations below the reference voltage cannot be subtracted from the total
overshoot/undershoot pulse duration.
7.9.5.3 Activity Factor
Activity factor (AF) describes the frequency of overshoot (or undershoot) occurrence
relative to a clock. Since the highest frequency of assertion of any common clock signal
is every other clock, an AF = 0.1 indicates that the specific overshoot (or undershoot)
waveform occurs every other clock cycle.
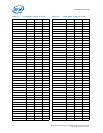
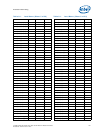
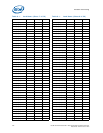
Table 7-23. Processor I/O Overshoot/Undershoot Specifications
Signal Group
Minimum
Undershoot
Maximum
Overshoot
Overshoot
Duration
Undershoot
Duration
Notes
Intel QuickPath Interconnect -0.2 * VTT 1.2 * VTT 39 ps 15 ps 1,2
DDR3 -0.2 * V
CCD
1.2 * V
CCD
0.25*T
CH
0.1*T
CH
1,2,3
System Reference Clock (BCLK{0/1}) -0.3V 1.15V N/A N/A 1,2
PWRGOOD Signal -0.420V VTT + 0.28 N/A N/A 4