Datasheet 75
5 Thermal Specifications
This chapter provides a description of the thermal features relating to the Itanium 2 processor.
5.1 Thermal Features
The Itanium 2 processor has an internal thermal circuit which senses when a certain temperature is
reached on the processor core. This circuit is used for controlling various thermal states. In
addition, an on-chip thermal diode is available for use by the thermal sensing device on the
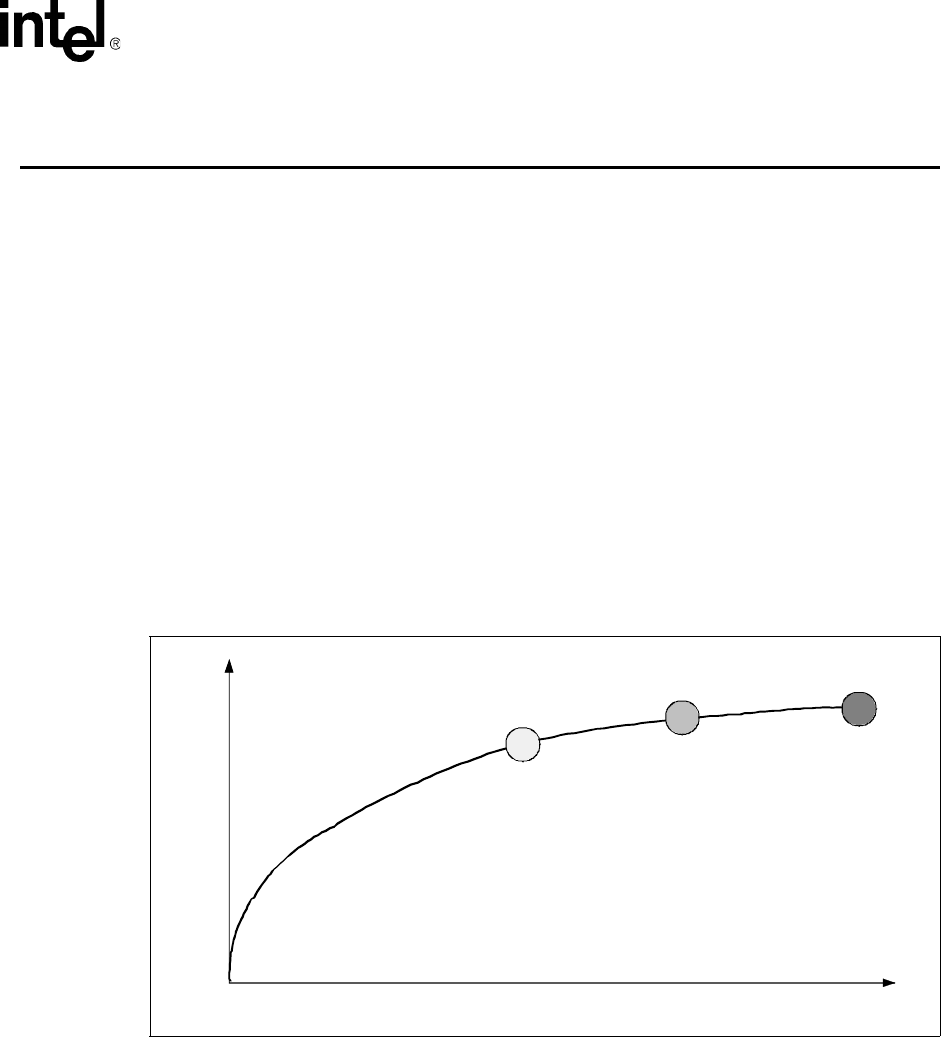
Itanium 2 processor. Figure 5-1 shows the relationship between temperature, time, and the thermal
alert, enhanced thermal management (ETM), and thermal trip points.
Note: Figure 5-1 is not intended to show a linear relationship in time or temperature as a processor's
thermal state advances from one state to the next state when the cooling solution fails to control the
processor temperature, as this is affected by many factors such as cooling solution performance
degradation and processor workload variations.
5.1.1 Thermal Alert
THRMALERT# is a programmable thermal alert signal which is part of the Itanium 2 processor
system management feature. THRMALERT# is asserted when the measured temperature from the
processor thermal diode equals or exceeds the temperature threshold data programmed in the high
temp (THIGH) or low temp (TLOW) registers on the sensor. Intel recommends using the upper
temperature reference byte listed in the Processor Information ROM when programming the
THIGH register (see Chapter 6 for more details). This signal can be used by the platform to
implement thermal regulation features such as generating an external interrupt to tell the operating
system that the processor core die temperature is increasing.
Figure 5-1. Itanium
®
2 Processor Thermal Features
000653b
Temperature
Time
Thermal Alert
Thermal Trip
ETM