36 ZT8101 User’s Manual
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
Multicasting
Multicasting is a group of protocols and tools that enable a single source point to send packets to
groups of multiple destination points with persistent connections that last for some amount of time.
The main advantage of multicasting, when compared to broadcasting, is a decrease in the network
load.
• Broadcast packets are sent to all devices on a subnetwork.
• Unicast packets are sent from a single network device to another single network device.
• Multicast packets are sent to a group of network devices.
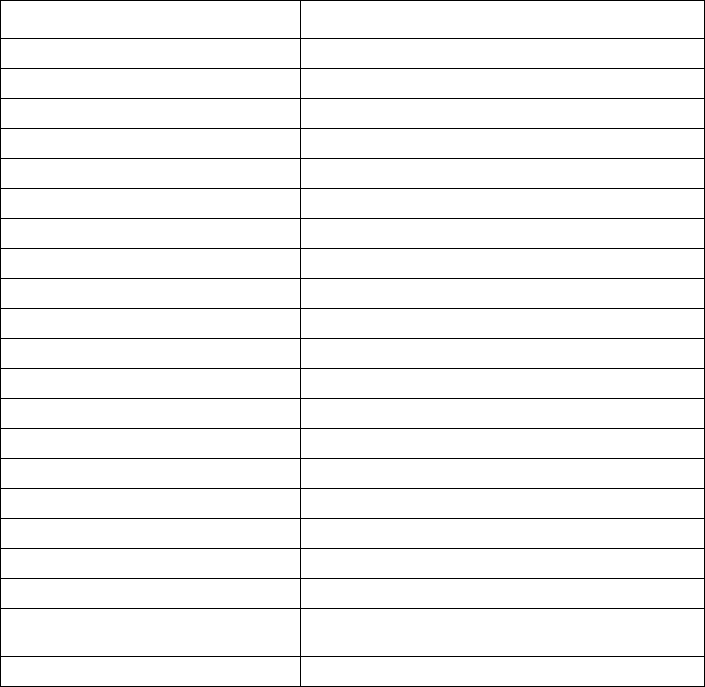
The following table lists some of the permanently assigned multicast addresses.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
Multicasting relies on the concept of nodes joining and leaving multicast groups. Nodes use IGMP
to join and then leave a multicast group. Based on the IGMP reports the switch receives from the
nodes, it can decide whether to forward a multicast packet on a particular interface.
Address Description
224.0.0.0 Base Address (reserved)
224.0.0.1 All Systems on this subnet
224.0.0.2 All Routers on this subnet
224.0.0.3 Unassigned
224.0.0.4 DVMRP Routers
224.0.0.5 OSPF IGP Routers
224.0.0.6 OSPF IGP Designated Routers
224.0.0.7 ST Routers
224.0.0.8 ST Hosts
224.0.0.9 All RIP2 Routers
224.0.0.10 All IGRP Routers
224.0.0.11 Mobile Agents
224.0.0.12 DHCP Servers and Relay Agents
224.0.0.13 All PIM Routers
224.0.0.14 RSVP Encapsulation
224.0.0.15 All CBT Routers
224.0.0.16 Designated Sbm
224.0.0.17 All Sbms
224.0.0.18 VRRP
224.0.0.19 through 224.0.0.225 except
224.0.0.21
Unassigned
224.0.0.21 DVMRP on MOSPF


















