161
Chapter 10:
SFE2000/SFE2000P Gigabit Ethernet Switch Reference Guide
Chapter
10
optimizes the STP protocol convergence. STP convergence can take 30-60 seconds in large
networks.
• Root Guard — Prevents devices outside the network core from being assigned the spanning tree
root.
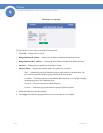
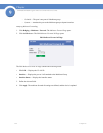
• Port State — Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what
forwarding action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are:
– Disabled — Indicates that STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic
while learning MAC addresses.
– Blocking — Indicates that the port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or learn
MAC addresses. Blocking is displayed when Classic STP is enabled.
– Listening — Indicates that the port is in Listening mode. The port cannot forward traffic nor
can it learn MAC addresses.
– Learning — Indicates that the port is in Learning mode. The port cannot forward traffic,
however it can learn new MAC addresses.
– Forwarding — Indicates that the port is in Forwarding mode. The port can forward traffic
and learn new MAC addresses.
• Port Role — Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to provide to STP paths. The
possible field values are:
– Root — Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the root switch.
– Designated — The port or LAG through which the designated switch is attached to the
LAN.
– Alternate — Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
– Backup — Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree
leaves. Backup ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a point-to-point
link, or when a LAN has two or more connections connected to a shared segment.
– Disabled — The port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.
• Path Cost — Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a
higher or lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path being rerouted.
• Priority — Priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice when a bridge has
two ports connected in a loop. The priority value is between 0 -240. The priority value is provided in
increments of 16.
• Designated Bridge ID — Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated
bridge.
• Designated Port ID — Indicates the selected port’s priority and interface.