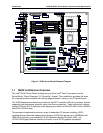
Intel® SHG2 DP Server Board Technical Product Specification Processor and Chipset
Revision 1.0 Intel Order Number C11343-001
9
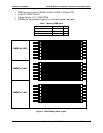
2.3 Memory Subsystem
Features provided in the SHG2 server board memory subsystem include the following:
•
Six DIMM sockets, supporting three pairs of PC1600 (DDR200), upward compatible with
PC2100 (DDR266) DIMMs.
•
Memory can be implemented with either single-sided (one row) or double-sided (two
row) DIMMs.
•
Minimum memory capacity of 256 MB (2 x 128MB DIMMs).
•
Maximum memory capacity of 12 GB (6 x 2GB DIMMs).
•
The DIMM organization is x72, which includes 8 ECC check bits.
•
Supports memory scrubbing, ECC single bit error correction, and multiple bit error
detection.
•
ECC from the DIMMs is passed through to the processor FSB.
•
Supports Chipkill* multiple bit error detection and multiple bit error correction.
•
Support for 2-way interleaved DDR SDRAM.
•
The DDR SDRAM interface is comprised of 2 channels running at a frequency of 200
MHz each for for a total interleaved transfer rate of 400MT /s.
Note: Memory interleaving is a way to increase memory performance by allowing the system to
access multiple memory modules simultaneously, rather than sequentially, in a similar fashion
to hard-drive striping. Interleaving can only take place between identical memory modules.
Note: Although the use of DDR266 modules is supported for upward compatibility, the channel
throughput is fixed at 400 MT/s, and the use of higher speed DIMMs will not provide additional
bandwidth. Mixed memory is not recommended, all DIMM sites should be populated with the
same speed and, when possible, same manufacturer.
2.3.1 Chipkill*
The CMIC-LE chipset supports Chipkill memory technology, which allows the system to recover
when a multi-bit error is encountered within a single DDR SDRAM device on the same DIMM
module. Chipkill memory technology provides protection up to, and including, a complete failure
of a single DRAM device. The Chipkill technology incorporated in the CMIC-LE does not
require any layout requirements on the memory boards. CMIC-LE contains the Chipkill
algorithm and performs all the data correction logic required.
Chipkill memory technology works by re-ordering the data from the DDR SDRAMs so that if one
DDR SDRAM device within a module should fail, the check bit algorithm provides sufficient
information to recover from the multi-bit data error. The correctable errors are then written to
the system error log (SEL) for evaluation at a later time.
2.3.2 Memory Configuration
Memory configuration requirements are as follows:
•
DDR200 or DDR266 SDRAM-registered DIMM modules
•
DIMM organization: x72 ECC
•
Pin count: 184