Setting Driver Properties
36 ViewCast
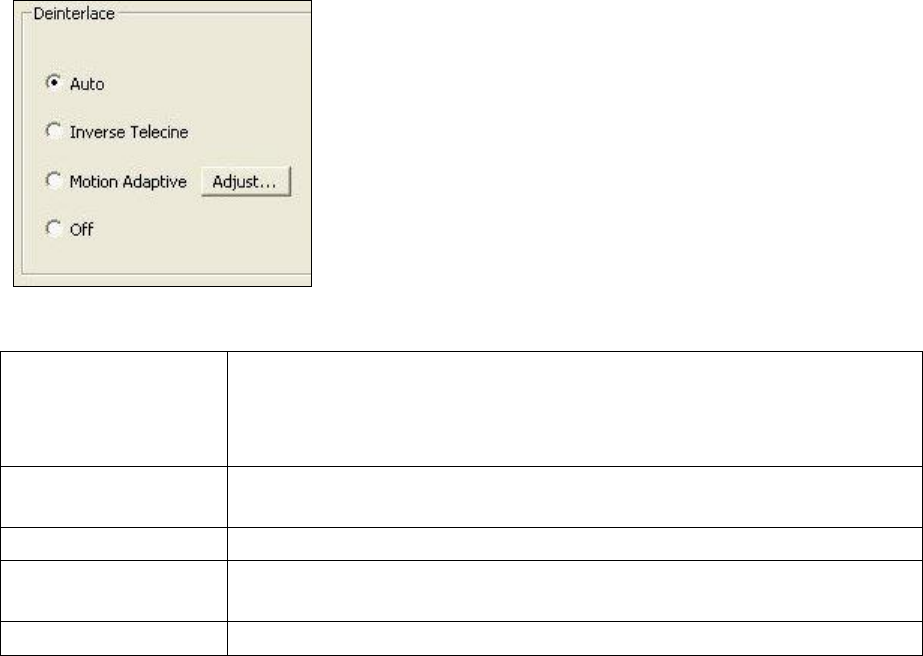
Deinterlace
Figure 35. Deinterlace settings
The deinterlace group has four radio buttons.
Auto
Apply inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Apply motion
adaptive deinterlacing to all video that is not telecine. Switch dynamically
between the two modes as the content changes. Available for NTSC video
only.
Inverse Telecine
Apply inverse telecine deinterlacing to all telecine video. Perform no
deinterlacing of video that is not telecine. Available for NTSC video only.
Motion Adaptive
Apply motion adaptive deinterlacing to all video.
Adjust…
Click this button to display the Adaptive Deinterlace window (see Adaptive
Deinterlace window).
Off
Perform no deinterlacing of any kind.
Deinterlace settings are applied and stored per-device and are applied to all filters and pins associated
with a device.
Changes to this control take effect as soon as you click Apply or OK.
When to deinterlace
When in doubt, deinterlace. In some cases bad artifacts will be seen if you do not deinterlace.
NTSC (29.97 fps) users: When in doubt, use Motion Adaptive deinterlacing rather than
Inverse Telecine. Motion Adaptive deinterlacing is not ideal for all content, but it works at
least adequately with all content. Inverse Telecine is ideal for telecine content – it
completely removes interlacing artifacts – but for non-telecine content, Inverse Telecine is
the same as no deinterlacing at all.
NTSC (29.97fps) users: When the content is known to be 100 % telecine, it is best to use
Inverse Telecine. Video sharpness will be superior (see Background
telecine and inverse
telecine).
PAL / SECAM (25 fps) users: When content is known to be 100 % progressive – that is, shot
by a film, universal, or progressive camera, it is best to turn off deinterlacing. Video
sharpness will be superior.