30 Chapter 3
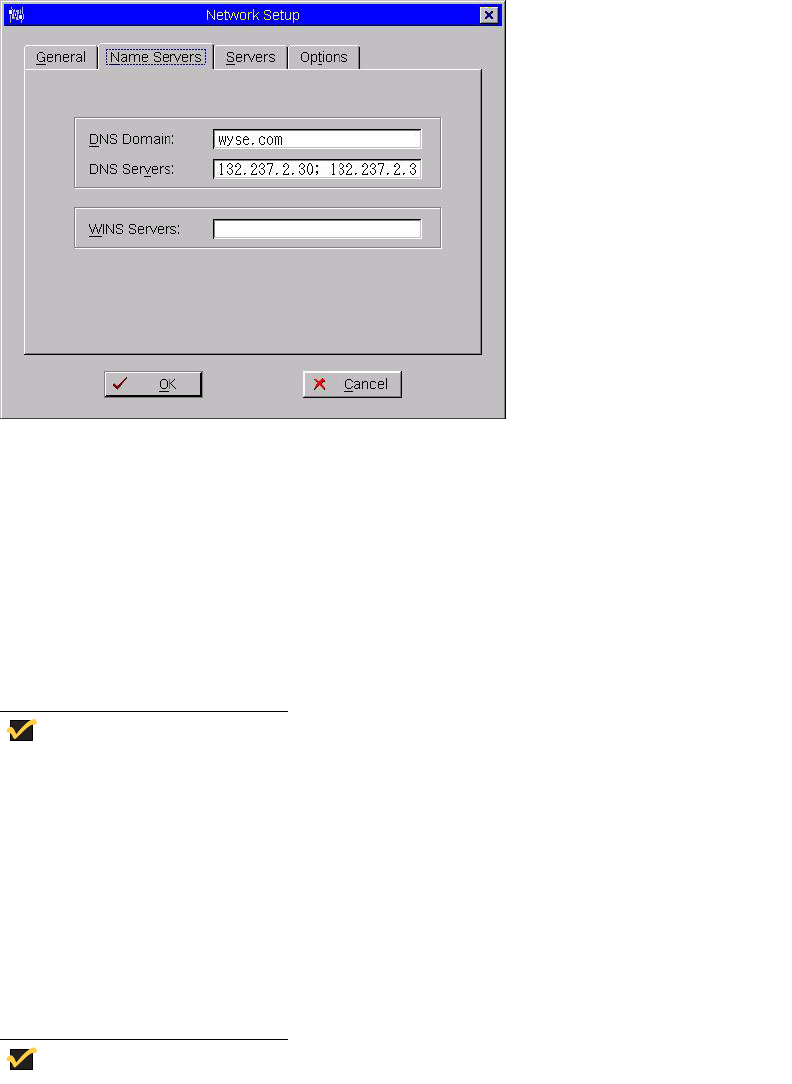
Figure 13 Network Setup - Name Servers tab
Use the following guidelines:
• DNS Domain and DNS Servers - Use of DNS is optional. DNS allows you to specify
remote systems by their host names rather than IP addresses. If a specific IP address
(instead of a name) is entered for a connection, it rather than DNS will be used to make
the connection. Enter the DNS Domain and the network address of an available DNS
Server. The function of the DNS Domain entry is to provide a default suffix to be used
in name resolution. The values for these two boxes may be supplied by a DHCP
server. If the DHCP server supplies these values, they will replace any locally
configured values. If the DHCP server does not supply these values, the locally
configured values will be used.
Note
You may enter two DNS Server addresses, separated by a semicolon,
comma, or space. The first address is for the primary DNS server and the
second is for a backup DNS server.
• WINS Servers - Use of WINS is optional. Enter the network address of an available
WINS name server. WINS allows you to specify remote systems by their host names
rather than IP addresses. If a specific IP address (instead of a name) is entered for a
connection, it rather than WINS will be used to make the connection. These entries can
be supplied through DHCP if DHCP is used. DNS and WINS provide essentially the
same function, name resolution. If both DNS and WINS are available, the thin client will
attempt to resolve the name using DNS first and then WINS.
Note
You may enter two WINS Server addresses, separated by a semicolon,
comma, or space. The first address is for the primary WINS server and the
second is for a backup WINS server.


















