5 Using the Network Test Tools
This chapter contains information on using the Network test tools available on the thin
client.
Ping (Packet InterNet Groper) and Trace Route can be used for checking the integrity of
the network connection (ping also checks the usability of the network configuration and
the availability of all equipment required to communicate between the thin client and the
ping destination). These tools can be accessed from the Network Test submenu of the
Desktop menu (generally, ping and Trace Route are used for system diagnostics by, or
under the direction of, a network administrator).
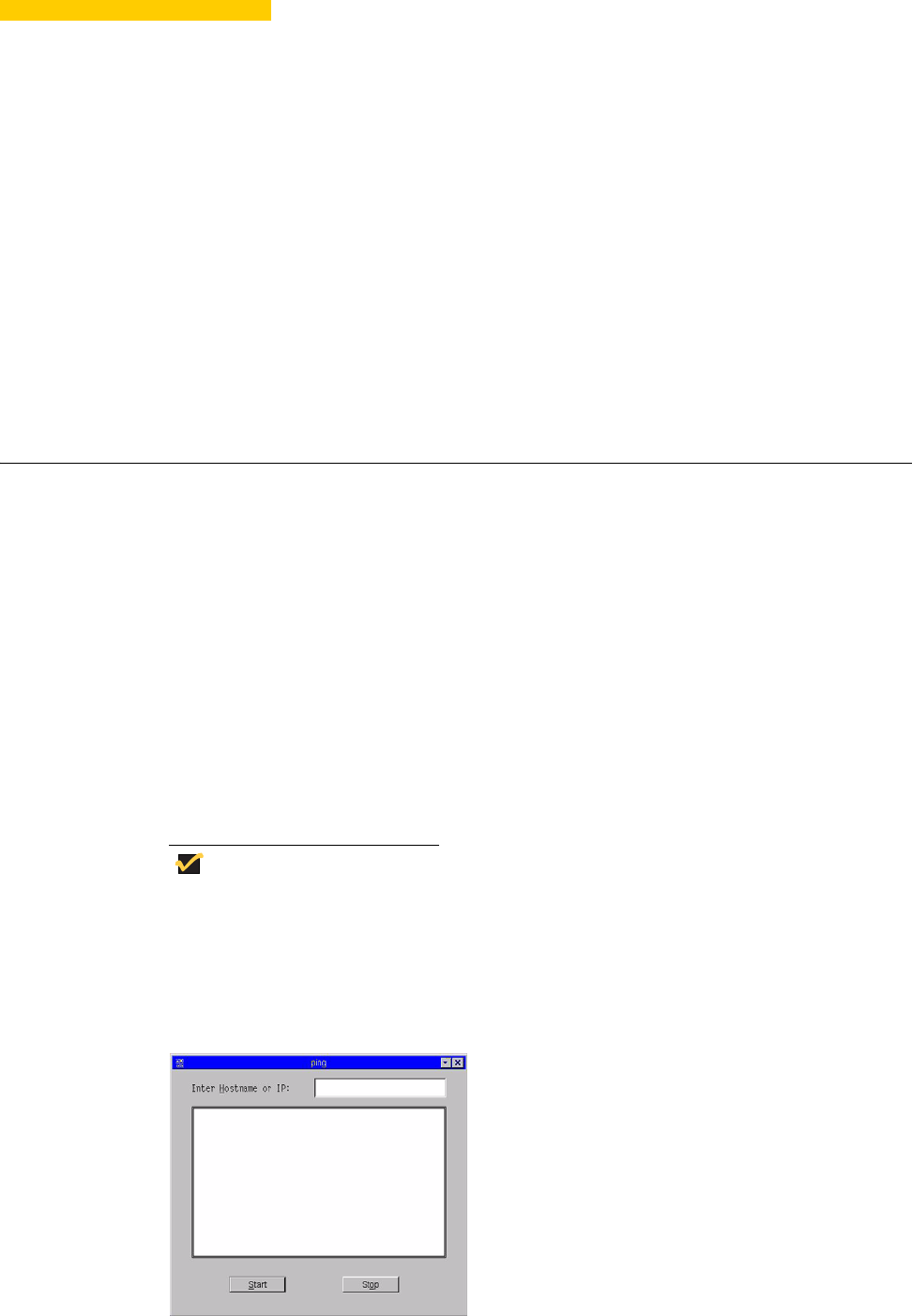
Using Ping
The ping dialog box executes the ping diagnostic utility and displays response messages.
Ping is a diagnostic tool that sends an echo request to a network host. The host parameter
is either a valid host name or an IP address. If the host is operational and on the network,
it responds to the echo request. By default, echo requests are sent until interrupted (by
clicking Stop in the ping dialog box). The ping utility sends one echo request per second
and calculates round trip times and packet loss statistics, and displays a brief summary
upon completion of the calculation.
The ping utility can be used to:
• Determine the status of the network and various foreign hosts
• Track and isolate hardware and software problems
• Test, measure, and manage networks
• Determine the IP address of a host if only the hostname is known
Note
Not all network equipment will respond to ping packets, since this is a
common mechanism used in denial-of-service attacks. Lack of response
does not necessarily indicate that the target of the ping is unusable for other
purposes.
Figure 32 ping


















