46 Zebra S-Series User’s Guide
,QWHUIDFHV
The method of interfacing the Zebra S-Series Printer to a data source
depends on the communication options installed in the printer. Depending
on how the printer was ordered, the interface is either an RS-232 serial
data port or a parallel port.
'DWD6SHFLILFDWLRQV
When communicating via the serial data port (RS-232), the baud rate,
number of data bits, and the parity are user-selectable (see Table 1 on
page 40 for acceptable setting combinations). Parity only applies to data
transmitted by the printer, since it ignores the parity of received data. The
S-Series Printer is fixed at 1 stop bit, so make sure that your host is also set
at 1 stop bit.
When communicating via the parallel port, the previously mentioned
parameters are not considered.
566HULDO'DWD3RUW
The connections for the standard interface are made through the DB-25S
connector on the rear panel. For all RS-232 input and output signals, the
S-Series Printer follows both the Electronics Industries Association’s
(EIA) RS-232 and the Consultative Committee for International Telegraph
and Telephone (CCITT) V.24 standard signal level specifications.
563LQRXWV
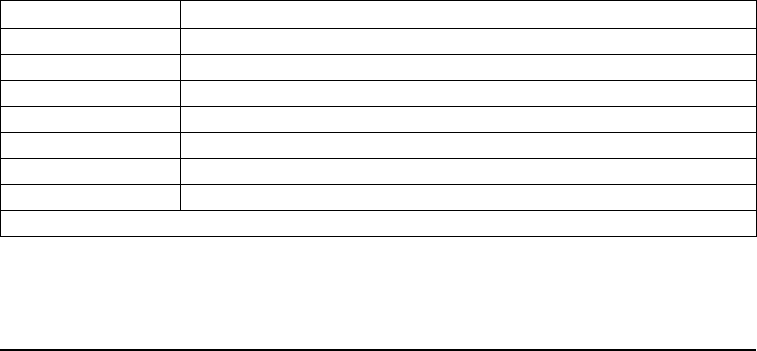
Table 3
Pin No. Description
1 Frame Ground for Cable Shield
2 TXD (Transmit Data) output from the printer
3 RXD (Receive Data) input to the printer
4 RTS (Request to Send) output from the printer
6 DSR (Data Set Ready) input to the printer
7 Signal Ground
20 DTR (Data Terminal Ready) output from the printer
Note: Pins 5, 8, 10-19, and 21-25 are unused and unterminated.


















