Bridging and Routing Models 3-5
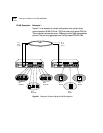
Figure 3-4 Bridging in the Traditional Bridging and Routing Model
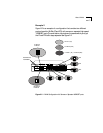
In the traditional bridging and routing model, a packet is routed as
follows (see Figure 3-5):
1 The packet enters the bridge or router.
2 The bridge or router determines that the packet belongs to a
recognized routing protocol, so the packet is passed to the router.
3 The router examines the destination network address and forwards the
packet to the interface (port) connected to the destination subnet.
Figure 3-5 Routing in the Traditional Bridging and Routing Model
1
Transmitting host
Destination host
Interfaces (ports)
Router Bridge
2
Networks
3
Router vs. Bridge ?
1
Transmitting host
3
Destination host
Interfaces (ports)
Router
Bridge
2
Networks
Router vs. Bridge ?