Page 23-2
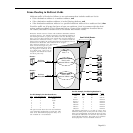
How Devices are Assigned to Multicast VLANs
If the recipients of the multicast traffic were defined using the port rule, each specified port is
then marked as a member of the multicast VLAN.
If the recipients of the multicast traffic were defined using the
MAC address rule to specify the
MAC addresses of the receiving devices, no action is taken until a frame is received from one
of those devices. When such a frame is received, the switch learns the device, adds its MAC
address to the filtering database, and marks the port on which the frame was received as a
member of the multicast VLAN. Note that the MAC address does not itself become a member
of the multicast VLAN, even though it is a recipient of the multicast traffic. Only ports are
members of multicast VLANs.
When the switch receive multicast traffic that has an address specified as a multicast address
for the multicast
VLAN, the traffic is switched to the ports defined as VLAN members.
♦ Please Take Note ♦
The source port of the multicast traffic (i.e., the port
through which multicast traffic enters the switch) can
be a member of any Group. The source port does not
need to be a member of the same Group as recipient
ports. Note that the source port does not become a
member of the multicast
VLAN.
Although some leakage may occur before devices are assigned to AutoTracker
VLANs, no
leakage occurs in conjunction with device assignment to multicast VLANs.
♦ Please Take Note ♦
There is no default multicast
VLAN. Unless you
explicitly create multicast VLANs, none will exist.
Multicast VLANs and Multicast Claiming
The goal of multicast claiming and multicast VLANs is the same—to free the MPX module from
processing multicast traffic. Both methods off-load multicast traffic processing to the switch-
ing modules. However, multicast
VLANs can be seen as a refinement to multicast claiming.
Multicast claiming claims the
MAC addresses of all source devices sending multicast traffic and
places those MAC addresses in the CAMs of all switching modules in a switch. Instead of
claiming all multicast traffic, multicast VLANs claim only the traffic from the multicast address
you specify. In addition, this multicast address is only placed in the CAMs of switching
modules with destination ports that are part of the multicast VLAN.