46
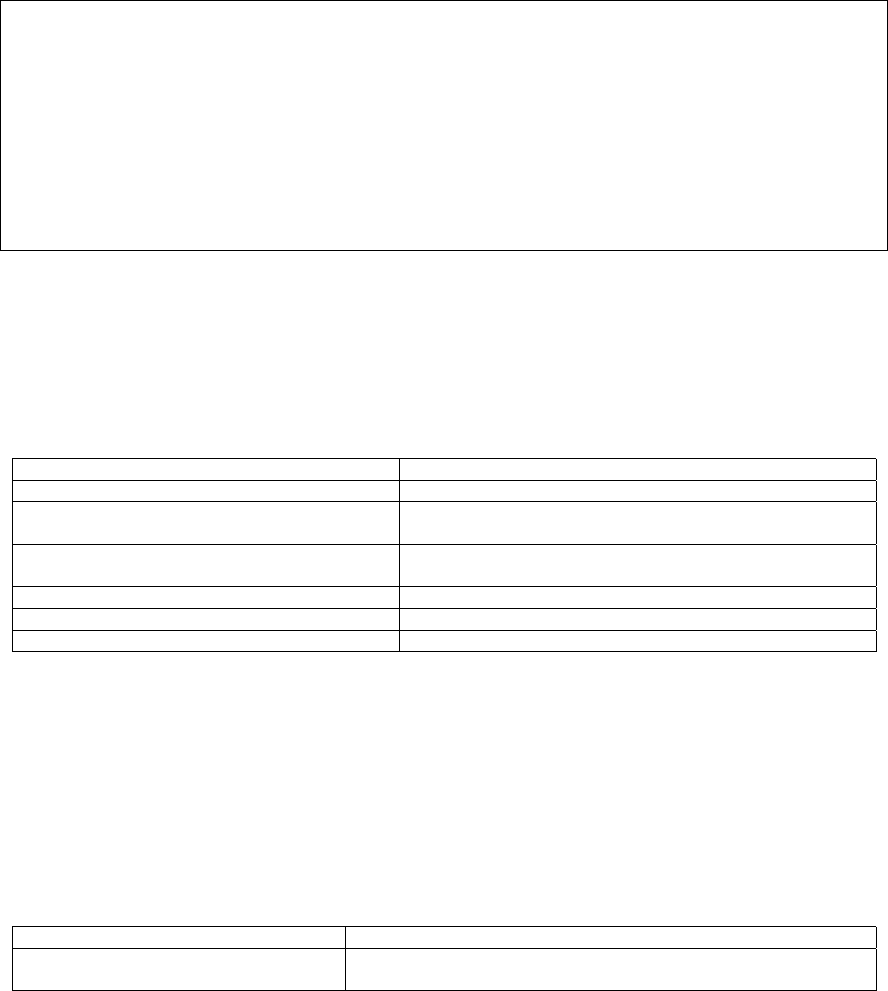
Router(config)# route-map map-tag permit 10
Router(config-route-map)# ?
end End current mode and change to enable mode.
exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
help Description of the interactive help system
match Match values from routing table
no Negate a command or set its defaults
on-match Exit policy on matches
quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
route-map Create route-map or enter route-map command mode
set Set values in destination routing protocol
Router(config-route-map)#
One or more
match
and
set
commands typically follow a
route-map
command. If there are no
match
commands, then everything matches. If there are no set commands, nothing is done. Therefore, you need
at least one match or set command. You can enter match commands into a route map in any order. If the
match criteria are met, and permit is on, then the route is redistributed or controlled as defined by the set
commands and route-map processing is complete. If the match criteria are met, and deny is on, then the
route is not redistributed or controlled and route-map processing is complete. To define conditions for
redistributing routes from a source route entry into the RIP tables, perform at least one of the following tasks
in route-map configuration mode:
Command Purpose
match interface interface-name
Match the specified interface.
match ip address {access-list-
name | prefix-list prefix-list-name}
Match a standard access list or prefix list.
match ip next-hop access-list-name
Match a next-hop router address passed by one of the
access lists specified.
match metric metric-value
Match the specified metric.
set ip next-hop
ip-address
Specify the address of the next hop.
set metric metric-value
Set the metric value to give the redistributed routes.
5.4.5 Set Metrics for Redistributed Routes
The metrics of one routing protocol do not necessarily translate into the metrics of another. For example, the
RIP metric is a hop count and the OSPF metric is a combination of five quantities.
In such situations, an artificial metric is assigned to the redistributed route. Because of this unavoidable
tampering with dynamic information, carelessly exchanging routing information between different routing
protocols can create routing loops, which can seriously degrade network operation.
To use the current routing protocol’s metric value for all redistributed routes, enter the following command in
router configuration mode.
Command Purpose
default-metric metric-value
Cause the current routing protocol to use the same metric value
for all redistributed routes.
Note: The metric value range is very large for compatibility with other protocols (0-2494967295).
For RIP, valid metric value is from 1 to 16.
5.4.6 Set Administrative Distance
The administrative distance is a value that rates the trustworthiness of a routing information source, such as
an individual router or a group of routers. In a large network, some routing protocols and some routers can
be more reliable than others as sources of routing information. Also, when multiple routing processes are
running in the same router for IP, it is possible for the same route to be advertised by more than one routing


















