59
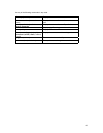
To configure the OSPF network type, use the following command in interface configuration mode.
Command Purpose
ip ospf network {broadcast |
non-broadcast |
point-to-multipoint | point-to-point}
Configure the OSPF network type for a
specified interface.
5.7.6 Configure OSPF for Non-broadcast Networks
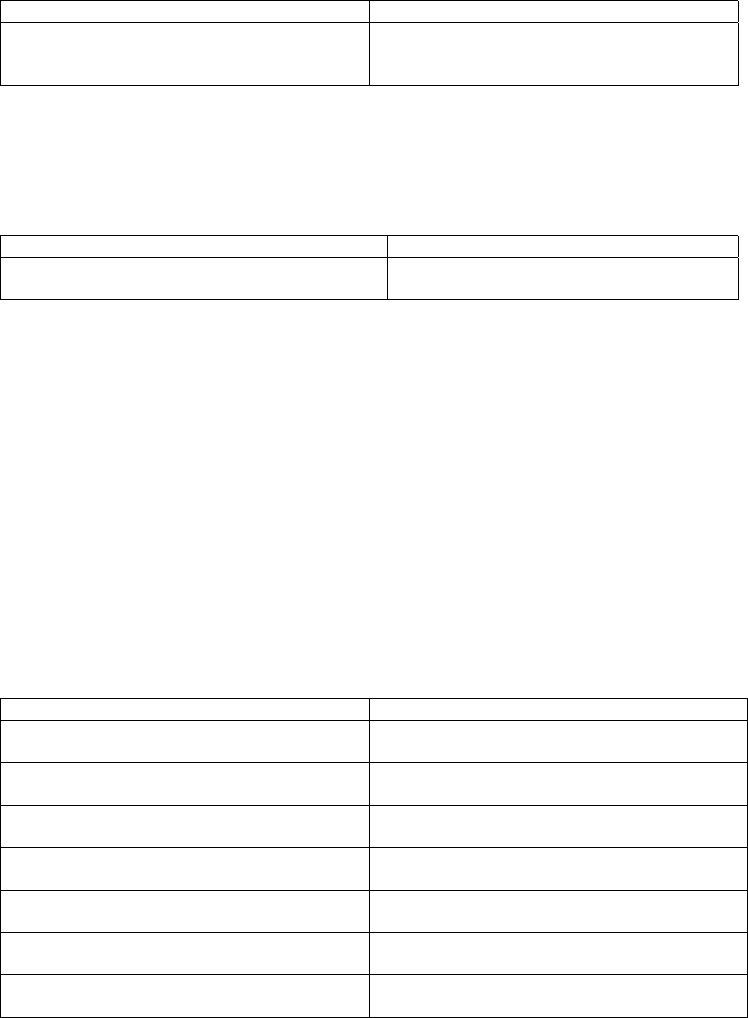
To configure routers that interconnect to non-broadcast networks, perform the following task in router
configuration mode.
Command Purpose
neighbor ip-address [priority number]
[
poll-interval
seconds]
Configure routers interconnecting to
non-broadcast networks.
As there might be many routers attached to an OSPF network, a designated router is selected for the
network. It is necessary to use priority and poll-interval parameters in the designated router selection if
broadcast capability is not configured. These parameters need only be configured in those devices that are
eligible to become the designated router or backup designated router.
5.7.7 Configure Area Parameters
The user can configure several area parameters including authentication, defining stub areas, and assigning
specific costs to the default route.
Authentication allows password-based protection against unauthorized access to an area. Stub areas are
areas into which information on external routes is not sent. Instead, there is a default external route
(generated by the area border router) into the stub area for destinations outside the autonomous system. To
further reduce the number of link state advertisements sent into a stub area, no-summary configuration on
the ABR is allowed to prevent it from sending summary link advertisement into the stub area.
In router configuration mode, specify any of the following area parameters as needed for the network.
Command Purpose
area {area-id | area-address}
authentication
Enable authentication for an OSPF area.
area {area-id | area-address}
authentication message-digest
Enable MD5 authentication for an OSPF
area.
area {area-id | area-address}
stub [no-summary]
Define an area as a stub area.
area
{area-id | area-address}
default-cost cost
Assign a specific cost to the default
summary route used for the stub area.
area {area-id | area-address}
export-list access-list
Define an area to be advertised into the
other areas.
area {area-id | area-address}
import-list access-list
Define an area to be allowed in the specified
area.
area
{area-id | area-address}
shortcut {default |disable |enable}
Set shortcutting behavior through an area.
5.7.8 Configure OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
The NSSA is similar to OSPF stub area. NSSA does not flood Type 5 external link state advertisements
(LSAs) from the core into the area, but it has the ability of importing AS external routes in a limited fashion
within the area.
The OSPF Specification (RFC 1583) prohibits the summarizing or filtering of Type 5 LSAs. It is an OSPF
requirement that Type 5 LSAs always be flooding throughout a routing domain. NSSA allows importing