60
specific external routes as Type 7 LSAs into the NSSA. In addition, when translating Type 7 LSAs into Type
5 LSAs by NSSA ABR, summarization and filtering are supported during the translation.
Use NSSA to simplify administration if you are an Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a network administrator
that must connect a central site using OSPF to a remote site that is using a different routing protocol such as
RIP.
Prior to NSSA, the connection between the corporate site border router and the remote router could not be
run as OSPF stub area because routes for the remote site cannot be redistributed into stub area. With
NSSA, you can extend OSPF to cover the remote connection by defining the area between the corporate
router and the remote router as an NSSA.
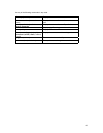
In router configuration mode, specify the following area parameters as needed to configure OSPF NSSA.
Command Purpose
area area-id nssa [no-summary|
translate-always | translate-candidate |
translate-never]
Set an area to be a NSSA.
If the user configures an NSSA totally stub area using no summary command, inter-area routes are not
allowed in the NSSA area. When redistribution takes places in the situations where there is no need to inject
external routes into the NSSA, you can prevent the router from creating Type 7 LSAs for NSSA using the
translate-never command. This situation can occur when an Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR)
is also an NSSA ABR. On the other hand, the translate-always command enables the router to redistribute
all external routes as Type 7 LSAs, which are translated into Type 5 LSAs by the NSSA ABR and then
leaked into the OSPF domain.
5.7.9 Configure Route Summarization between OSPF Areas
Route summarization causes a single summary route to be advertised to other areas by an ABR.
In OSPF, an ABR will advertise networks in one area into another area. If the network numbers in an area
are assigned in a way such that they are contiguous, you can configure the ABR to advertise a summary
route that covers all the individual networks within the area that fall into the specified range.
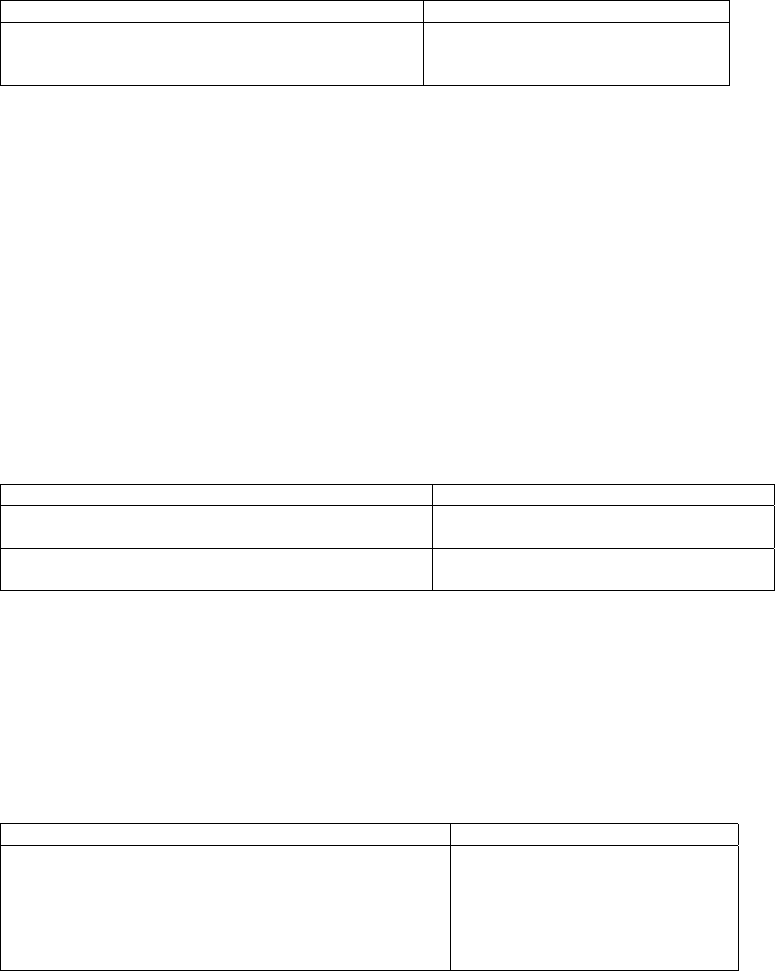
To define an address range, perform the following task in router configuration mode.
Command Purpose
area
{area-id | area-address}
range
prefix-length
[not-advertised]
Define an address range where a single
route will be advertised.
area
area-address
range
prefix
{suppress
|
substitute}
prefix
Announce an address range where a
route will not be injected.
5.7.10 Create Virtual Links
In OSPF, all areas must be connected to a backbone area. If there is a break in backbone continuity, or the
backbone is purposefully portioned, you can establish a virtual link. The virtual link must be configured in
both routers. The configuration information in each router consists of the other virtual endpoint, and the non-
backbone area that the two routers have in common (called the transit area). Note that virtual link cannot be
configured through stub areas.
To create a virtual link, perform the following task in router configuration mode.
Command Purpose
area
area-id
virtual-link
router-id [
hello-
interval seconds] [retransmit-interval
seconds] [
transmit-delay
seconds] [
dead-interval
seconds] [[
authentication-key
key]|[
message-digest-key
keyed
md5
key]]
Establish a virtual link.