70
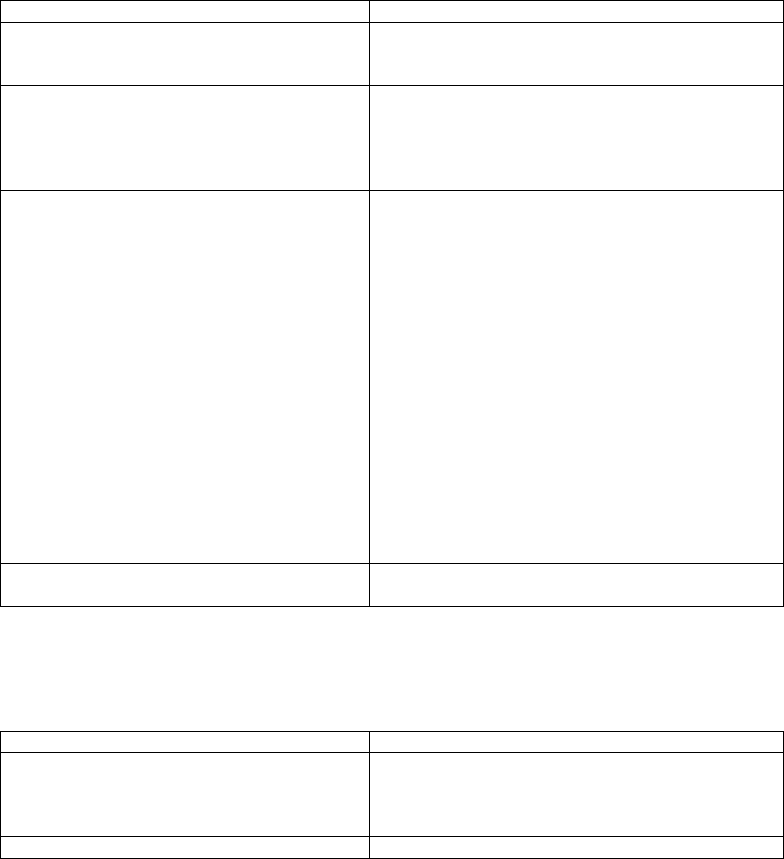
Use the following commands to configure the VLAN Allowed List for the trunk port:
Command
Purpose
Router(config)# interface IFNAME
Enter the interface name to access the interface
configuration node.
Router(config-if-IFNAME)# switchport
mode trunk
This command designates the interface as IEEE
802.1q trunk-access mode.
Use the no form of this command to reset to the
default of static-access mode.
Router(config-if-IFNAME)# switchport
trunk allowed vlan
{
add
|
all
|
except
|
remove} vlan-list
This command will configure the VLAN Allowed
List for the trunk port.
add - Add VLANs to the current VLAN list
all – Add all VLANs to the allowed-VLAN list
except – Add all VLANs except those specified
in the VLAN list
remove – Remove the VLANs specified in the
VLAN list.
vlan-list – The VLAN list can be a single VLAN
or a range of VLANs (from 1-4094). Separate the
VID number by a comma, or by a hyphen when
listing a range (i.e. 120, 158, 4090-4094)
Use the no form of this command to reset to
default setting of all VLANs in the VLAN Allowed
List.
Router(config-if-IFNAME)# end
Return to Enable node.
The trunk port accepts tagged and untagged frames. All the untagged frames are classified to the trunk
port’s native VLAN (the VLAN whose VID matches the port’s VLAN ID). The trunk port also sends out the
frames as untagged for the native VLAN. Using the following global configuration command can change this
behavior:
Command
Purpose
Router(config)# vlan dot1q tag native
This global command enables tagging of native
VLAN frames on all 802.1Q trunk ports.
Use the
no
form of this command to disable
tagging of native VLAN frames.
Router(config)# end
Return to Enable node.
6.2.3 Dot1q Tunnel
802.1Q tunnel ports are used to maintain customer VLAN integrity across a service provider network. You
can configure a tunnel port on an edge switch in the service provider network and connect it to an 802.1Q
trunk port on a customer interface, creating an asymmetric link. A tunnel port belongs to a single VLAN that
is dedicated to tunneling.