67
Chapter 6. VLAN Configuration
Up to 4094 Virtual LANs (VLANs) are supported on the IC35516. The switch is shipped with a default VLAN
with VLAN ID (VID) 1. All switchports (eth1-eth16) are included in the default VID 1. The default VID 1
cannot be deleted.
6.1 Creating or Modifying a VLAN
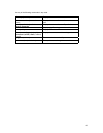
Command Purpose
Router(config)# vlan vid
Enter a VLAN ID (2-4094), which will access
config-vlan mode. Enter a new VLAN ID to
create a VLAN, or enter an existing VLAN ID to
modify a VLAN.
Router(config-vlan)# name Engineering
VLAN
Enter a name for the VLAN (optional).
Router(config)# end
Return to Enable node.
Deleting a VLAN
Command Purpose
Router(config)# no vlan vid
Enter a VLAN ID (2-4094) to be removed.
Switchports are Layer 2-only interfaces associated with a physical port. A switchport is used as an access
port. Switch ports are used for managing the physical interface and associated Layer 2 protocols and do not
handle routing or bridging. Ports 1 through 16 on the 35516 are Ethernet ports. The following example
demonstrates how to enter the interface configuration mode for port 16:
Router(config)# interface eth16
Router(config-if-eth16)#
From the interface configuration mode, use the switchport command to configure the access port or the
Class of Service (CoS) default priority for the port.
An access port belongs to and carries the traffic of only one VLAN (see Virtual Interfaces, below.) Traffic is
received and sent in native formats with no VLAN tagging. Traffic arriving on an access port is assumed to
belong to the VLAN assigned to the port. If an access port receives a tagged packet (802.1Q tagged), the
packet is dropped, and the source address is not learned. Static access ports are manually assigned to a
VLAN.
Router(config-if-eth16)# switchport access vlan <1-4094>
Virtual Interfaces
A virtual interface represents a VLAN of switchports as one interface to the routing or bridging function in the
system. Only one virtual interface can be associated with a VLAN, but it is only necessary to configure a
virtual interface for a VLAN when you wish to route between VLANs or to provide IP host connectivity to the
switch. By default, a virtual interface (veth1) is created for the default VLAN (VLAN 1) to permit remote
switch administration. Additional virtual interfaces must be configured. In Layer 2 mode, virtual interfaces
provide IP host connectivity only to the system; in Layer 3 mode, you can configure routing across virtual
interfaces.
In order to create a virtual interface, it must be bound to a VLAN that has already been configured and
bound in turn to a physical port or ports. The following examples show how to create a VLAN (with a VLAN
ID of 2), how to select a port (interface eth9) to belong to the VLAN, and how to create a virtual interface
(veth2) by binding it to VLAN 2.