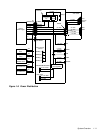
System Overview 1-7
NIC
GXpro systems contain either an integrated 10-Mbps or 10/100-Mbps 3Com
NIC. GXpro systems containing the 10-Mbps Ethernet NIC have a built-in inte-
grated 3Com 3C915 NIC chip. GXpro systems containing the 10/100-Mbps
Ethernet NIC have a built-in integrated 3Com 3C916 Ethernet NIC chip. The
NIC subsystem connects to the Ethernet network through a single RJ45 connec-
tor on the back panel of the computer.
The 10/100-Mbps NIC supports a 10-Mbps direct connection to either a cate-
gory-3 or a category-5 ethernet cable. When the NIC operates in the
100-Mbps mode, a category-5 ethernet cable must be used.
GXpro systems with the 10/100-Mbps NIC also contain two USB connectors.
Thus, to determine whether a particular system contains the 10/100-Mbps NIC,
look for one of the following indications:
•
USB connectors next to the NIC connector on the computer’s back panel
•
The message USB Enhanced displayed during the boot routine
•
A USB category on page 2 of the System Setup
If any of these indications are present, your system has the 10/100-Mbps NIC.
Chapter 5, “Using the Network Interface Controller,” in the User’s Guide pro-
vides instructions for connecting the system to, and configuring it for use on, an
Ethernet network.
USB
USB capability simplifies connection of peripheral devices such as mice, print-
ers, and computer speakers. The USB connectors on your computer’s back
panel provide a single connection point for multiple USB-compliant devices.
USB-compliant devices can also be connected and disconnected while the sys-
tem is running.
NOTE: USB capability is available only on systems with the 10/100-Mbps NIC.
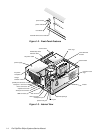
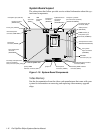
Desktop Chassis
The system unit can be set horizontally or vertically, when used with the floor
stand provided with the system. The floor stand attaches to the left side of the
system.
Thermal Monitoring
The primary and, if installed, secondary microprocessors have a thermal sensor
that monitors the processor’s temperature. If the critical threshold is exceeded, a
system alarm triggers a system management interrupt (SMI), which alerts the
BIOS. The power indicator flashes, and a message appears on the monitor to
alert the user that the system will shut down in an orderly manner, preventing
the loss of data.