xStack
®
DES-3200-10/18/28/28F Layer 2 Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
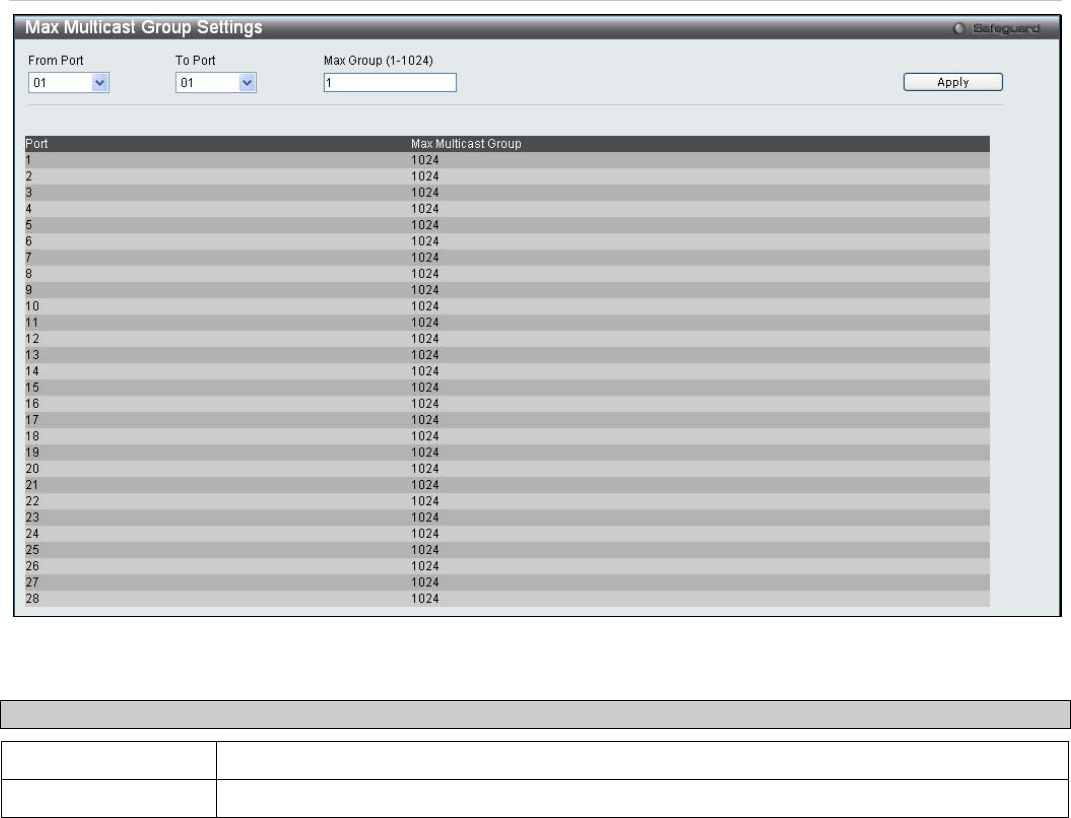
Figure 3 - 35. Max Multicast Group Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
From Port/To Port
Use the drop-down menus to choose a range of ports.
Max Group (1-1024)
Enter the maximum number of the multicast groups. The range is from 1 to 1024.
MLD Snooping Settings
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping is an IPv6 function used similarly to IGMP snooping in IPv4. It is used to
discover ports on a VLAN that are requesting multicast data. Instead of flooding all ports on a selected VLAN with
multicast traffic, MLD snooping will only forward multicast data to ports that wish to receive this data through the use
of queries and reports produced by the requesting ports and the source of the multicast traffic.
MLD snooping is accomplished through the examination of the layer 3 part of an MLD control packet transferred
between end nodes and a MLD router. When the Switch discovers that this route is requesting multicast traffic, it adds
the port directly attached to it into the correct IPv6 multicast table, and begins the process of forwarding multicast
traffic to that port. This entry in the multicast routing table records the port, the VLAN ID and the associated multicast
IPv6 multicast group address and then considers this port to be a active listening port. The active listening ports are
the only ones to receive multicast group data.
The Switch supports both MLD Snooping version 1 and MLD version 2.
MLD Control Messages
If implementing MLD snooping version 1, three types of messages are transferred between devices. These three
messages are all defined by three ICMPv6 packet headers, labeled 130, 131, and 132.
1. Multicast Listener Query, Version 1 – Similar to the IGMPv2 Host Membership Query for IPv4, and labeled
as 130 in the ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the router to ask if any link is requesting
multicast data. There are two types of MLD query messages emitted by the router. The General Query is used
to advertise all multicast addresses that are ready to send multicast data to all listening ports, and the
Multicast Specific query, which advertises a specific multicast address that is also ready. These two types of
messages are distinguished by a multicast destination address located in the IPv6 header and a multicast
address in the Multicast Listener Query Message.
85


















