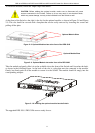
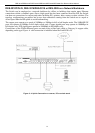
DES-3010F/DES-3010FL/DES-3010G/DES-3016/DES-3018/DES-3026 Fast Ethernet Switch Manual
19
The DES-3026 switch supports SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. You can specify which version of SNMP you
want to use to monitor and control the Switch. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of security
provided between the management station and the network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v.2c, user authentication is accomplished using 'community strings', which function like
passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the Switch SNMP must use the same community string.
SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2c management access are:
• public - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
• private - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects.
SNMP v.3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts. The first part is
to maintain a list of users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SNMP managers. The second part
describes what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager.
The Switch allows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges. The SNMP
version may also be set for a listed group of SNMP managers. Thus, you may create a group of SNMP
managers that are allowed to view read-only information or receive traps using SNMP v.1 while assigning a
higher level of security to another group, granting read/write privileges using SNMP v.3.
Using SNMP v.3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be restricted
from performing specific SNMP management functions. The functions allowed or restricted are defined
using the Object Identifier (OID) associated with a specific MIB. An additional layer of security is available
for SNMP v.3 in that SNMP messages may be encrypted. To read more about how to configure SNMP v.3
settings for the Switch read the section entitled Management.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the Switch. The events can be as
serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status change.
The Switch generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network manager). Typical traps include
trap messages for Authentication Failure, Topology Change and New Root.
MIBs
Management and counter information are stored by the Switch in the Management Information Base (MIB).
The Switch uses the standard MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values for MIB
objects can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network management software. In addition to the standard
MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended Management
Information Base. The proprietary MIB may also be retrieved by specifying the MIB Object Identifier. MIB
values can be either read-only or read-write.