29
Creating arrays
www.gateway.com
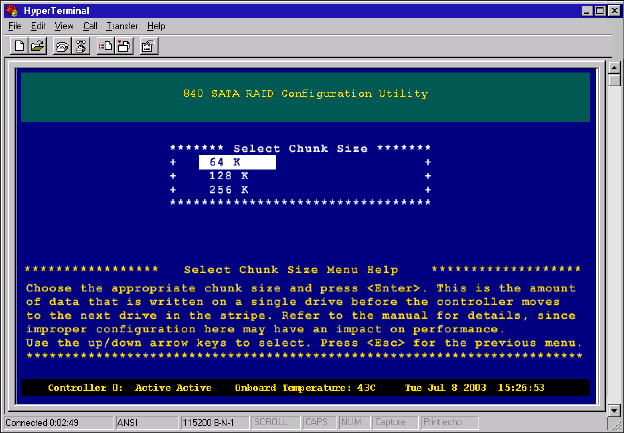
6 Select Manual Configuration, then press ENTER. The Select Chunk Size screen
opens.
The available chunk sizes are 64 K, 128 K, and 256 K. This is the amount
of data that is written on a single drive before the controller moves to the
next drive in the stripe.
To achieve optimum RAID 5 write performance you should consider setting
the chunk size based on the specified number of drives for a Full Stripe
Write when configuring RAID 5/50 arrays. See “Optimizing RAID 5 Write
Performance” on page 227 for detailed information.
The primary aim of setting a chunk size is to try to set a stripe size that
allows for full stripe writes. The stripe size is determined by the number
of data drives multiplied times the chunk size, (8 data drives × 64 K chunk
size = 512 strip size).
For maximum performance with RAID 5/50 arrays, you want to do as many
full stripe writes as possible. Typically, Windows NT, Windows 2000, and
Windows 2003 access at 64 K. Therefore, a stripe size of up to 1 MB would
mean the controller has to cluster 16 commands to perform a full stripe
write (actually 17 because of alignment). If you were to use a larger stripe
size, you run the risk of not being able to cluster sufficiently for the
application.
