Statistics Programs 16–11
File name 32sii-Manual-E-0424
Printed Date : 2003/4/24 Size : 17.7 x 25.2 cm
Logarithmic Exponential Power
To start:
W
L
W
E
W
P
R 0.9965 0.9945 0.9959
M –139.0088 51.1312 8.9730
B 65.8446 0.0177 0.6640
Y (
y
ˆ
when X=37)
98.7508 98.5870 98.6845
X (
x
ˆ
when Y=101)
38.2857 38.3628 38.3151
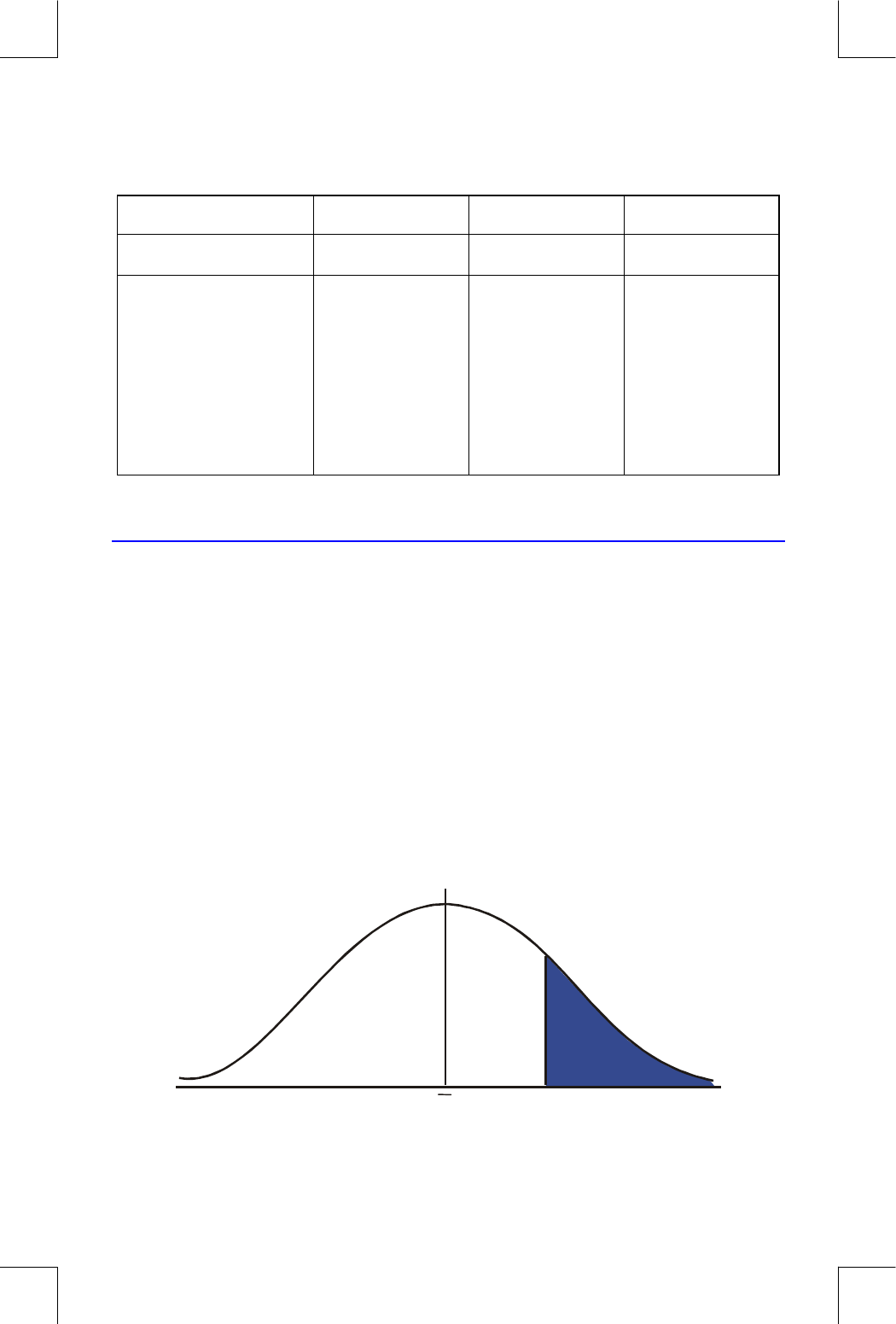
Normal and Inverse–Normal Distributions
Normal distribution is frequently used to model the behavior of random
variation about a mean. This model assumes that the sample distribution is
symmetric about the mean, M, with a standard deviation, S, and
approximates the shape of the bell–shaped curve shown below. Given a
value x, this program calculates the probability that a random selection from
the sample data will have a higher value. This is known as the upper tail area,
Q(x). This program also provides the inverse: given a value Q(x), the
program calculates the corresponding value x.
x
y
"U
pp
er tail"
area
x
Q [x]


















