Technical Reference Guide
5.8.4 AUDIO CODEC
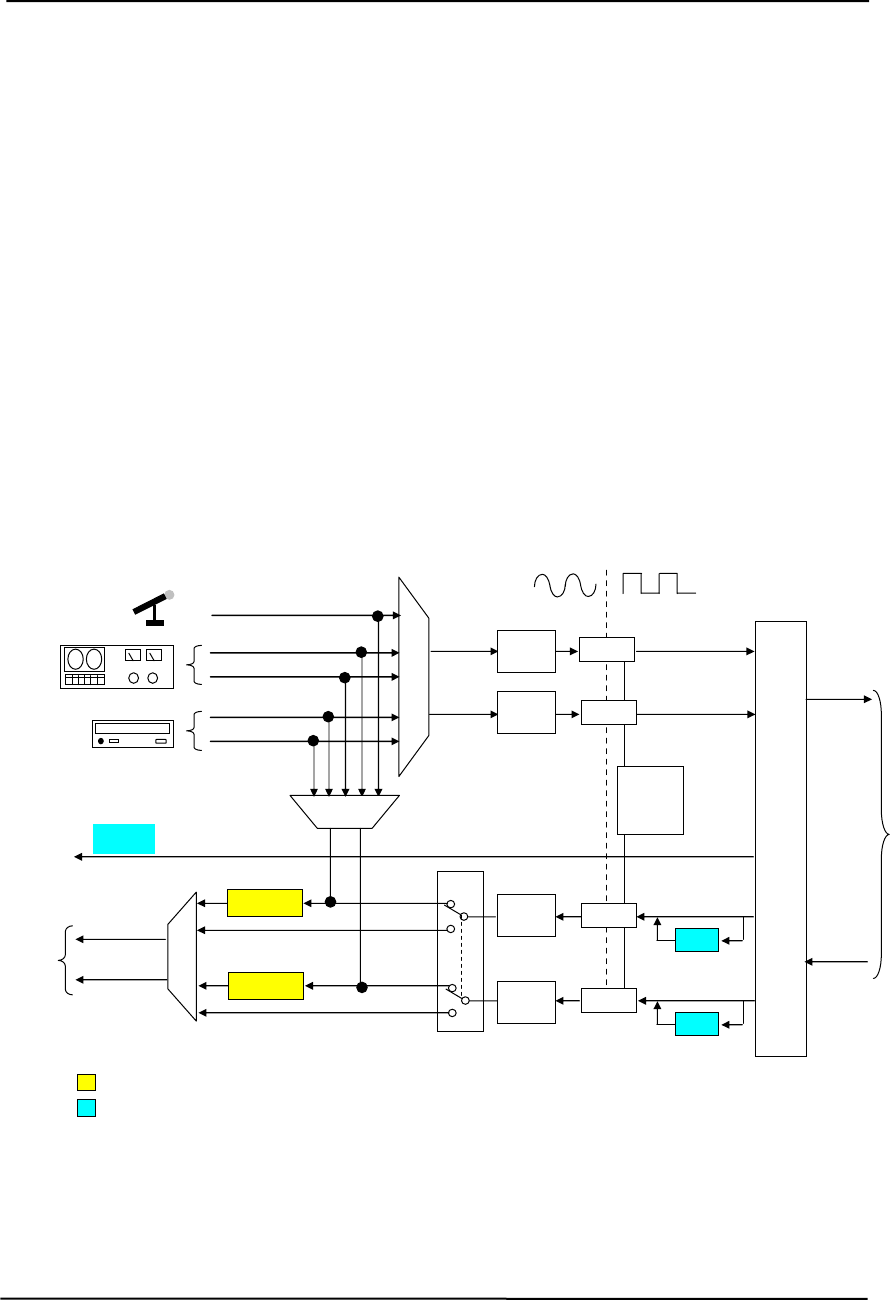
The audio codec provides pulse code modulation (PCM) coding and decoding of audio
information as well as the selection and/or mixing of analog channels. As shown in Figure 5-12,
analog audio from a microphone, tape, or CD can be selected and, if to be recorded (saved) onto a
disk drive, routed through an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The resulting left and right PCM
record data are muxed into a time-division-multiplexed (TDM) data stream (SD IN signal) that is
routed to the audio controller. Playback (PB) audio takes the reverse path from the audio
controller to the audio codec as SD OUT data and is decoded and processed by the digital-to-
analog converter (DAC). The codec supports simultaneous record and playback of stereo (left
and right) audio. The Sample Rate Generator may be set for sampling frequencies up to 48 KHz.
Analog audio may then be routed through 3D stereo enhancement processor or bypassed to the
output selector (SEL). The integrated analog mixer provides the computer control-console
functionality handling multiple audio inputs.
The D315 and D325 models use the Analog Devices AD1885 and the AD1981B respectively.
These devices differ in that the AD1885 includes a 3D analog processor while the AD1981B
includes an equalizer as well as SPDIF support.
Audio
Format
SPDIF
AD1981B only
AD1885 only
EQ
EQ
ADC
PB
Data (R)
PB
Data (L)
DAC
DAC
Rec
Data (R)
ADC
Rec
Data (L)
S
E
L
(R)
(L)
(R)
(R)
(L)
(L)
3D Proc.
3D Proc.
SW
PB
Gain
PB
Gain
Rec
Gain
Rec
Gain
Σ/Mixer
CD In (R)
CD In (L)
Line In (R)
Line In (L)
Mic In
S
e
l
e
c
t
o
r
SD Out
SD IN
AC97
Link
I/F
Sample
Rate
Gen.
Right
Audio
Analog
Output
Circuits
Left
Audio
Audio
Controller
Figure 5-12. Audio Codec Functional Block Diagram and Difference Matrix
5.8.5 AUDIO PROGRAMMING
Compaq D315 and hp d325 Personal Computers
Featuring the AMD Athlon XP Processor
Second Edition - April 2003
5-29


















