Technical Reference Guide
AGP 2X Transfers
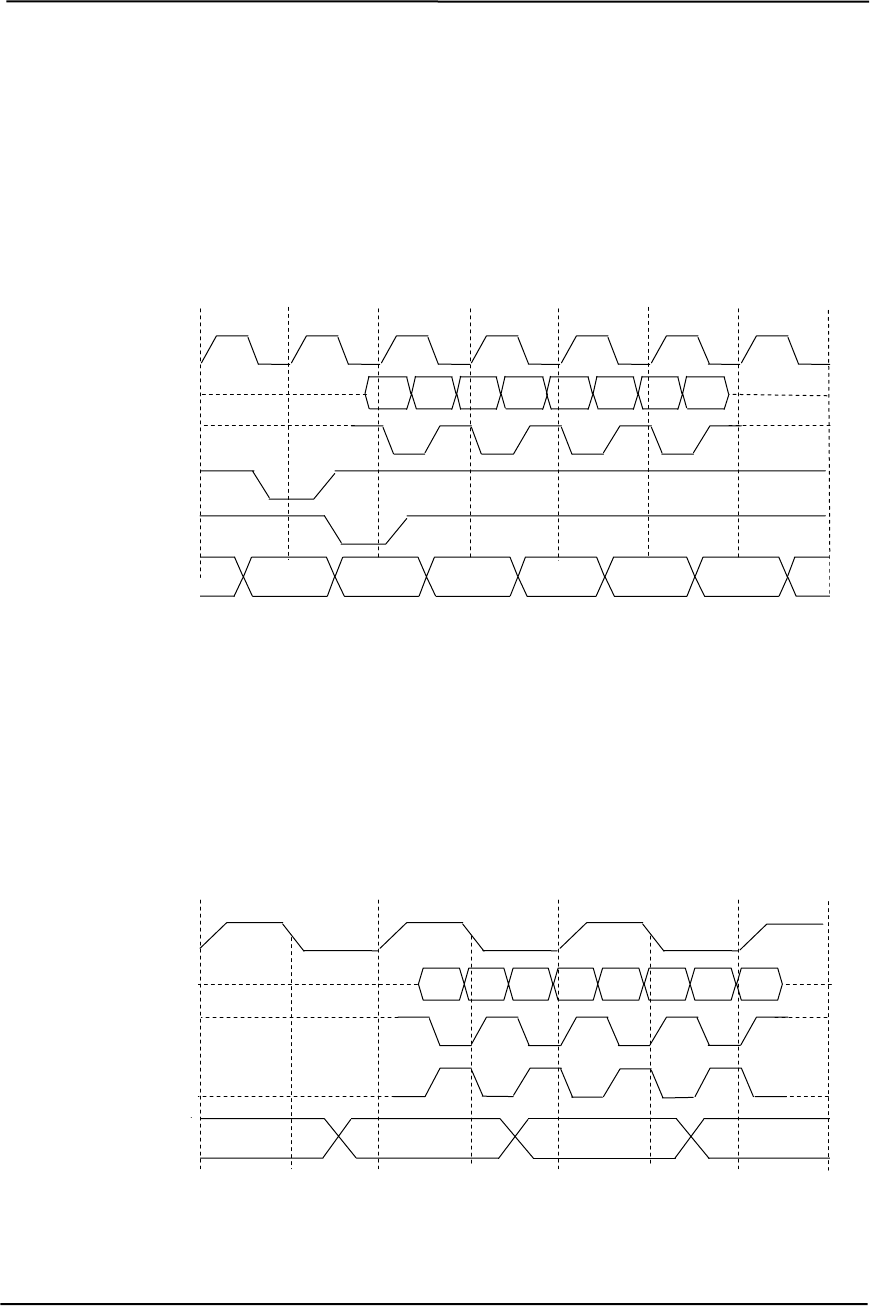
During AGP 2X transfers, clocking is basically the same as in 1X transfers except that the 66-
MHz CLK signal is used to qualify only the control signals. The data bytes are latched by an
additional strobe (AD_STBx) signal so that an 8-byte transfer occurs in one CLK cycle (Figure 4-
6). The first four bytes (DnA) are latched by the receiving agent on the falling edge of AD_STBx
and the second four bytes (DnB) are latched on the rising edge of AD_STBx. The signal level for
AGP 2X transfers may be 3.3 or 1.5 VDC.
xxx
xxx
xxx
xxx
xxx
00x
ST0..2
D2A D3A
D2B D3B D4A D4B
D1A
D1B
AD
AD_STBx
CLK
GNT-
TRDY-
T6 T7 T5 T4 T3 T2 T1
Figure 4-6. AGP 2X Data Transfer (Peak Transfer Rate: 532 MB/s)
AGP 4X Transfers
The AGP 4X transfer rate allows sixteen bytes of data to be transferred in one clock cycle. As in
2X transfers the 66-MHz CLK signal is used only for qualifying control signals while strobe
signals are used to latch each 4-byte transfer on the AD lines. As shown in Figure 4-7, 4-byte
block DnA is latched by the falling edge of AD_STBx while DnB is latched by the falling edge of
AD_STBx-. The signal level for AGP 4X transfers is 1.5 VDC.
ST0..2
xxx xxx xxx 00x
AD_STBx-
CLK
D1A D2A D1B D3A D3B D4A D4B D2B
AD
AD_STBx
T2 T3
T4
T1
Figure 4-7. AGP 4X Data Transfer (Peak Transfer Rate: 1064 MB/s)
Compaq D315 and hp d325 Personal Computers
Featuring the AMD Athlon XP Processor
Second Edition - April 2003
4-11
