KS152JB Universal Communications Controller
Technical Specifications
Kawasaki LSI USA, Inc. Page 84 of 120 Ver. 0.9 KS152JB2
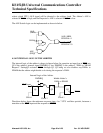
selects which CPU’s ALE signal will be directed to the address latch. The Arbiter’s ALE is
selected if
HLDA is high, and the Requester’s ALE is selected if HLDA is low.
The ALE Switch logic can be implemented as shown in below.
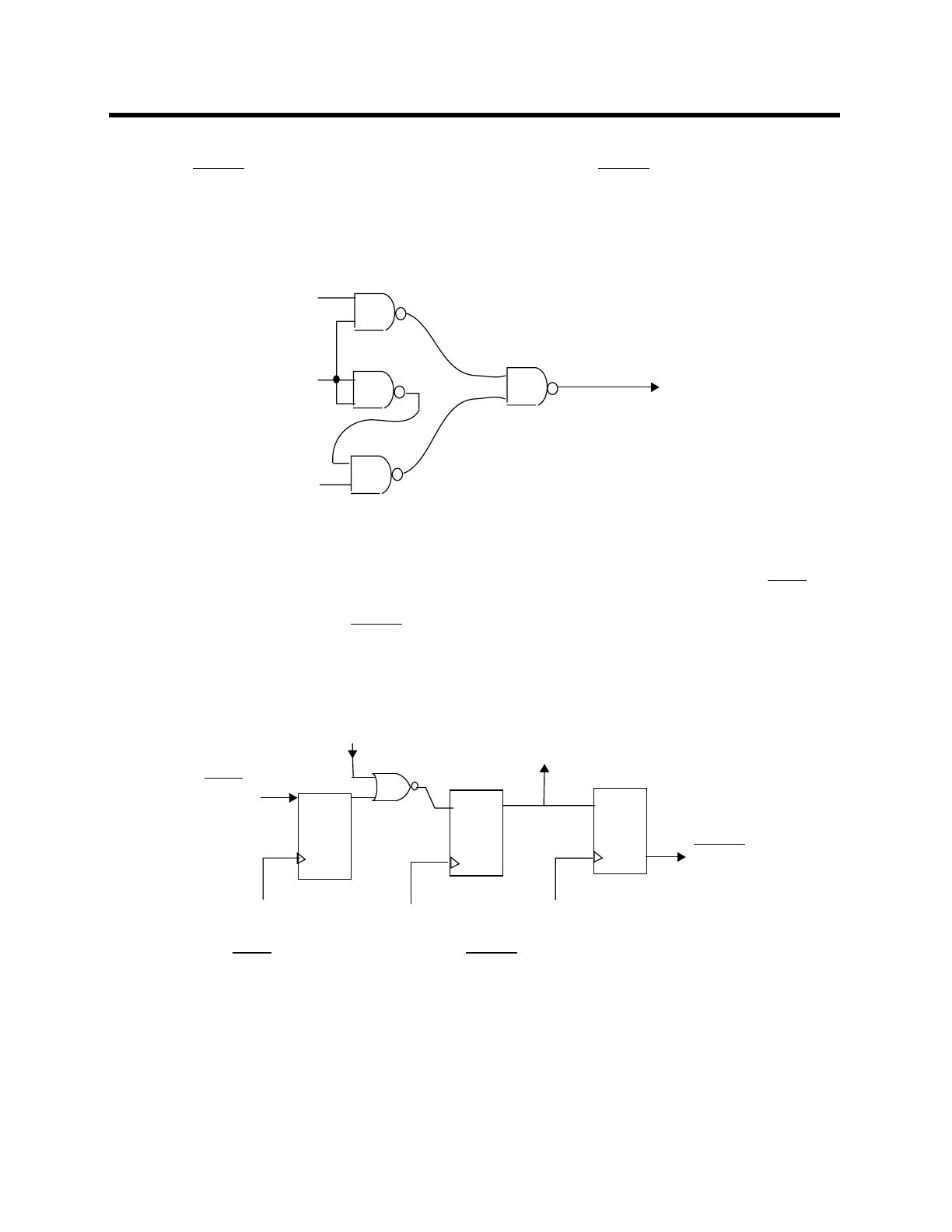
4.3.4 INTERNAL LOGIC OF THE ARBITER
The internal logic of the arbiter is shown in figure below. In operation an input low at
HLD sets
Q2 if the arbiter’s internal signal DMXRQ is low. DMXRQ is the arbiter’s “DMA to XRAM
Request”. SettingQ2 activates
HLDA through Q3. Q2 being set also disables any DMAs to
XRAM that the arbiter might decide to do during the requester’s DMA.
Internal Logic of the Arbiter
Waveform below shows the minimum response time, 4 to 7 CPU oscillator periods, between a
transition at the
HLD input and the response at HLDA.
ALE
(ARB)
HLDA
ALE
(REQ)
ALE (ARB)
IF HLDA = 1
ALE (AEQ)
IF HLDA = 0
HLD Input
Clock 1
Clock 2
Clock 1
Q2
D
Q
D
Q
Q1
Q3
D
Q
HLDA
Inhibit Arbiter’s
DMA to XRAM
DMXRQ