Section Three Function Description
© National Instruments Corporation 3-3 GPIB-COM User Manual
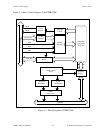
GPIB-COM Components
The interface consists of the following functional components:
• Address Decoding
• Configuration Jumpers
• INS8250A Compatible Registers
• GPIB Acceptor and Source Handshaking
• Mode Control Logic
• Interrupt Control Logic
• Direction Buffers
• GPIB Transceivers
Address Decoding
Address decoding monitors the PC address bus to recognize when a GPIB-COM address is
present and enables a read and/or write to its registers.
Configuration Jumpers
These onboard jumpers select the base address, GPIB controller mode, and interrupt request line
used by the GPIB-COM.
INS8250A Compatible Registers
The main component of an IBM PC compatible serial adapter is an INS8250A Asynchronous
Communications chip or its equivalent, which handles RS-232 communication. The INS8250A
compatible registers on the GPIB-COM emulate the serial adapter registers so that the GPIB-
COM will operate transparently with any serial port driver.
GPIB Acceptor and Source Handshaking
This circuitry converts PC serial port handshaking into GPIB handshaking. This process is
completely software-transparent.
Mode Control Logic
This circuitry determines whether the GPIB-COM should be a Talker (and the target device a
Listener) or a Listener (and the target device a Talker).
Interrupt Control Logic
This circuitry generates and masks interrupts on GPIB conditions which correspond to the
conditions that would cause the INS8250A circuit to generate an interrupt.