Appendix B: Algorithms
B–4
TDS 500C, TDS 600B, & TDS 700C User Manual
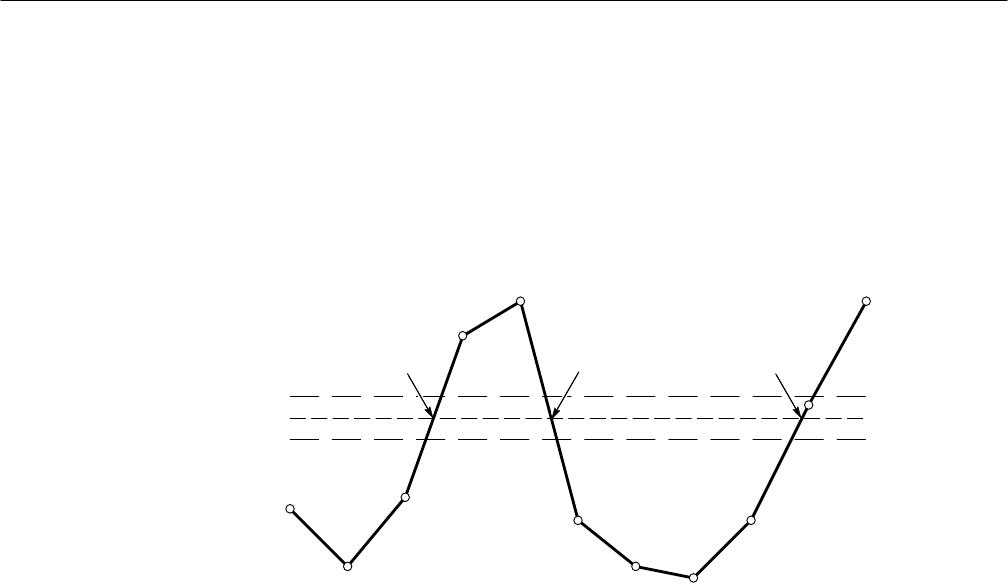
MCross1, MCross2, and MCross3 — refer to the first, second, and third MidRef
cross times, respectively. (See Figure B–1.)
The polarity of the crossings does not matter for these variables, but the
crossings alternate in polarity; that is, MCross1 could be a positive or negative
crossing, but if MCross1 is a positive crossing, MCross2 will be a negative
crossing.
MidRef + (Hysteresis x Amplitude)
MidRef – (Hysteresis x Amplitude)
MidRef
MCross1
(StartCycle)
MCross2
MCross3
(EndCycle)
Figure B–1: MCross Calculations
The oscilloscope calculates these values as follows:
1. Find the first MidRefCrossing in the waveform record or the gated region.
This is MCross1.
2. Continuing from MCross1, find the next MidRefCrossing in the waveform
record (or the gated region) of the opposite polarity of MCross1. This is
MCross2.
3. Continuing from MCross2, find the next MidRefCrossing in the waveform
record (or the gated region) of the same polarity as MCross1. This is
MCross3.
MCross1Polarity — is the polarity of first crossing (no default). It can be rising or
falling.
MCross Calculations
