PPPoE Circuit-ID Tag Operation Process
The general PPPoE Circuit-ID Tag work process is shown below:
Figure 12-25 PPPoE Discovery Process
The PPPoE discovery process is illustrated below:
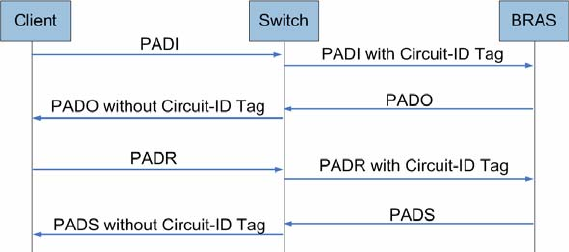
1. The client sends PADI (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation) packets to the switch.
2. The switch intercepts PADI packets and inserts a unique Circuit-ID tag to them.
3. The switch forwards the PADI packets with Circuit-ID tag to the BRAS.
4. The BRAS responses with the PADO (PPPoE Active Discovery Offer) packets after receiving
the PADI packets.
5. Upon receiving the PADO packets with the Circuit-ID tag, the switch will remove the tag and
send the packets to the client. The switch will forward the PADO packets without the Circuit-ID
tag directly.
6. The client sends PADR (PPPoE Active Discovery Request) packets according to the process.
7. The switch intercepts PADR packets and inserts a unique Circuit-ID tag to them.
8. The switch forwards the PADR packets with Circuit-ID tag to the BRAS.
9. The BRAS processes the received Circuit-ID tag in the PADR packets and extracts the
Circuit-ID field to the RADIUS for accounting. And the BRAS allocates a PPP process session
ID for this PPP session.
10. The BRAS responses with the PADS (PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation) packets
after receiving the PADR packets.
11. Upon receiving the PADS packets with the Circuit-ID tag, the switch will remove the tag and
send the packets to the client. The switch will forward the PADS packets without the Circuit-ID
tag directly.
On the PPPoE Circuit-ID page, you can enable the PPPoE Circuit-ID function globally. Each
port’s PPPoE Circuit-ID Insertion feature and type can be configured separately.
Choose the menu Network Security→PPPoE Config→PPPoE Circuit-ID to load the following
page.
218


















