PRINT FORMAT COMMANDS
6-92 XEROX DOCUPRINT 180 LPS PDL REFERENCE
• Using pitch and the TMODE parameter effectively
Paper sizes each have an associated pitch mode.
There are six processing modes available on your LPS. These
are called pitch modes. A pitch is a term describing the number
of pages that can be imaged on the printer photoreceptor belt.
A pitch mode is a phrase that describes how many pitches can
occur during one complete photoreceptor revolution. For
example, while processing in 7-pitch mode, seven images can
be placed on the photoreceptor belt during one revolution of the
belt.
As page size increases, fewer images can be placed on the
photoreceptor belt during one revolution. Since the belt runs at
a constant speed, a decrease in the number of images that can
be placed on the belt causes a corresponding drop in the
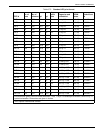
pages-per-minute (ppm) throughput of the LPS. Table 6-76
shows the various pitch modes, their corresponding ppms, and
the default paper sizes for each pitch mode. The paper size
used in a job determines the highest pitch mode in which the
system will run that job.
If you change paper sizes within a job, and this change crosses
a pitch boundary, the system performs a xerographic quality
adjustment, which may significantly impact performance.
Specifying the pitch (also called the throughput mode) with the
TMODE parameter of the OUTPUT command allows you to
control the default pitch mode with the following benefits:
— Matching system throughput with finishing device
restrictions: If the finishing device attached to the printer
cannot accept output at rated speed, the printer inserts
gaps in the paper path to ensure that pages do not arrive at
the device too rapidly. For example, if this is done at 180
ppm, it would effectively slow throughput to 68 ppm. This is
true even if the finishing device could accept pages at up to
120 ppm. If you adjusted this 7-pitch job into 6-pitch mode,
the job would run faster than 116 ppm.
— Eliminating process adjustment cycles during jobs that
cross pitch boundaries: Each time a job crosses a pitch
boundary, the system performs a xerographic quality
adjustment. If this is done frequently within a job, the
adjustments may take a substantial amount of the overall
print time. Lowering the pitch mode so that the entire job
runs at the same mode may enable you to significantly
increase performance.