AMD Confidential
User Manual September 12
th
, 2008
Chapter 3: Graphical User Interface 21
3.3.5.1 Example: 1GB DDR2 memory
When you instantiate a “Dimm Bank” known device into a created device, you get its
default state of 8 empty dimm‟s with no configuration. You can then configure the
“Dimm Bank”, such as by opening the device‟s GUI configuration properties to specify
general options (such as max number of dimm‟s), and to configure each dimm (such as
by importing an SPD). You could configure it, for example, to emulate a dimm bank with
2 DDR2 dimm‟s (1GB each).
Device groups offer us a potentially simpler alternative - for the user to instantiate a
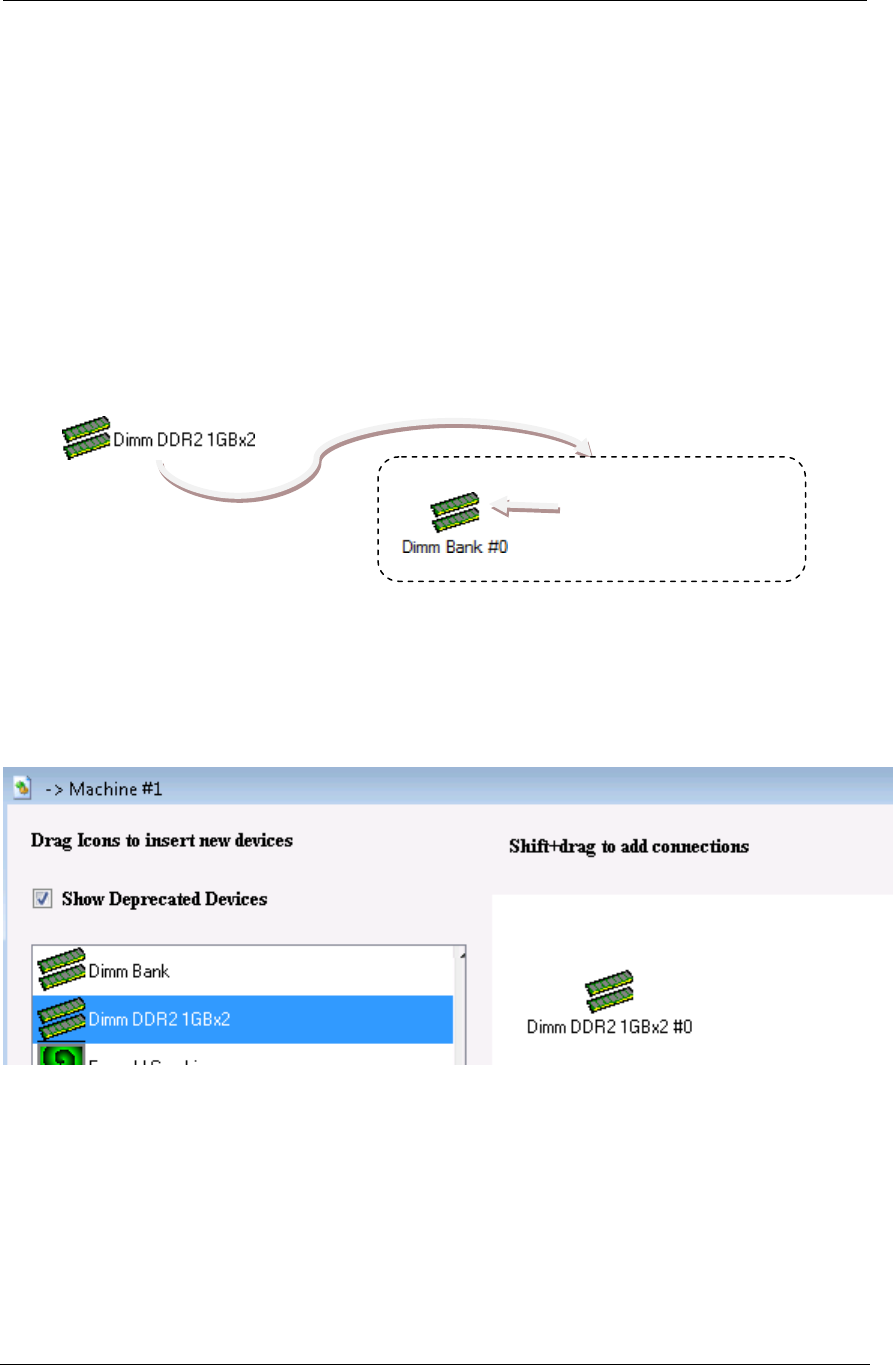
preconfigured device group. For example, we could have a device group “Dimm DDR2
1GBx2”, which has (inside it) only one child and default archive data (state) for that
child. The figure below shows that the (theoretical) known device “Dimm DDR2 1GBx2”
has inside it a single child device “Dimm Bank #0” that is configured with two dimm‟s
(type DDR2, 1GB each).
Figure 3-11: Example DIMM Device Group
When the user instantiates this (theoretical) known device “Dimm DDR2 1GBx2” as a
created device, we get a created device “Dimm DDR2 1GBx2 #0” with a child device
“Dimm Bank #0” that is already configured (as DDR2, 2 dimm, 1GB each). Our resulting
main device GUI would look like this:
Figure 3-12: Created DIMM Device Group
The device GUI for the children of “Dimm DDR2 1GBx2 #0” would look like this:
Configured as DDR2,
2 dimm (1GB each)


















