Advanced Management
Page 4-20
A VLAN localizes flooded traffic to parts of LAN segments rather than to a
whole LAN. VLANs offer a simple and efficient solution that enhances
network performance, bandwidth utilization, and network security by
localizing flooded traffic.
Port-based VLANs are the simplest of many VLAN approaches that solve
the problem of unnecessary flooding. A port-based VLAN allows the
administrator to assign individual ports on a switch to a VLAN. Any
broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast traffic received on a port in a
VLAN is flooded only to the other ports in the VLAN rather than to all ports
in the system. This greatly reduces unnecessary traffic in a network.
For the most complete information about configuring VLANs in an 802.1Q
environment, see the standard, available from IEEE <http://www.ieee.org>.
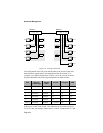
Tagged and Untagged Frames
In a network with only one switch, the switch itself can keep track of which
ports belong to which VLANs.
In a network with multiple switches, information about which VLAN an
ethernet frame belongs to must be sent along with the frame. This is done by
inserting a tag field in the frame, as defined in IEEE 802.1Q. The tag
includes the VID to identify the frame’s VLAN. When a port receives a
tagged frame, it can then pass the frame to other port members of the same
VLAN.
When you add a port to a VLAN, you can specify whether or not frames
originating from that port will be tagged. If the port is configured to send
tagged frames, then its traffic will be associated with the VLAN identified in
the tags.
If it receives an untagged frame, a port has no way to determine the
originating VLAN. In that case, the port can be configured to send the frame
as is, to aribtrarily assign a specific tag to the frame, or to drop the frame.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used throughout this section.
FID Filtering ID
GARP Generic Attribute Registration Protocol
GVRP GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
ISL Inter-Switch Link
MGMT Management