50
Configure drives
transmitted data at one end of the transaction, then the
parity data is checked at the other end to make sure the
transmission has not had any errors.
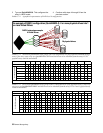
In the array, transmitted data with the added parity data
is striped across disk drives. A hardware XOR engine
computes parity, thus alleviating software processing
during reads and writes.
The array operates in degraded mode if a drive fails.
Interleave
The interleave size sets the amount of data to be
written to each drive in a RAID group. This is a
tunable parameter which takes a single stream of data
and breaks it up to use multiple disks per I/O interval.
The CLI command
RAIDInterleave
allows you to
change the size of the sector interleave between RAID
groups. The value will depend upon the normal
expected file transfer size. If the normal file transfer
size is large, the interleave value should be large, and
vice versa.
The value entered for the
RAIDInterleave
command
refers to blocks of data: one block is equivalent to 512
bytes of data.
Valid entries are 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 and SPAN.
SPAN, not available in RAID Level 5, indicates that
interleave size between the drives in the group will be
the minimum drive size of all members in the group.
Partitions
With the introduction of larger and larger GB-sized
drives, the array may have up to 7.2 TB total data
capacity. Partitioning can increase storage efficiency
by providing more LUNs without using lower capacity
RAID groups.
Partitioning allows the creation of multiple logical
volumes. Long LBA (64 bit addressing) allows you to
take full advantage of the increasing storage capacity
made possible through the new high capacity disk
drives. Applications and host operating systems which
do not support Long LBAs are able to access larger
array capacities which otherwise would not have been
possible.
Using the CLI or by accessing the
Advanced
CLI
configuration page in the ExpressNAV interface, you
are able to divide an individual Partition into a set of
equally-sized subpartitions which can then be
presented to hosts as separate LUNs.
Zones
Zoning is a collection of related Diamond capabilities
supporting flexible array configuration management
configurable via CLI commands in the CLI or the
Advanced
CLI configuration page of the
ExpressNAV interface. Zoning supports security by
granting or denying access between initiators and
devices as defined by an administrator.
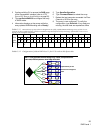
A zone is a collection of devices which can access
each other. The devices in a zone usually include one
or more initiators, one or more devices, and one or
more paths between the initiators and the devices.
Hot Spare sleds
In most configurations, if a member of a virtual device
becomes degraded, you must swap out the faulted sled
as defined in
Hot Swap Operating Instructions on page
87
. If you have not enabled
AutoRebuild
, you must
also start a manual rebuild.
For four configurations, however, Hot Spare sleds may
be designated as replacements for faulted sleds
without intervention by you or a host.
Each configuration requires a certain number of Hot
Spare sleds. These sleds, once designated as Hot
Spares, are not available for other use.
The following configurations support optional Hot
Spare sleds:
RAID Level 1:
2 Hot Spare sleds
RAID Level 10:
1 group, 2 Hot Spare sleds
RAID Level 5:
1 group, 1 Hot Spare sled
RAID Level 5:
2 groups, 2 Hot Spare sleds
Enhancing performance
SpeedWrite, enabled by the CLI command
SpeedWrite
, improves the performance of WRITE
commands