Chapter 3 Processor/Memory Subsystem
Compaq iPAQ Family of Internet Devices
First Edition - March 2000
3-2
3.2 PROCESSOR
The Compaq iPAQ is configured as either a Celeron-based or Pentium III-based system.
3.2.1 CELERON PROCESSOR
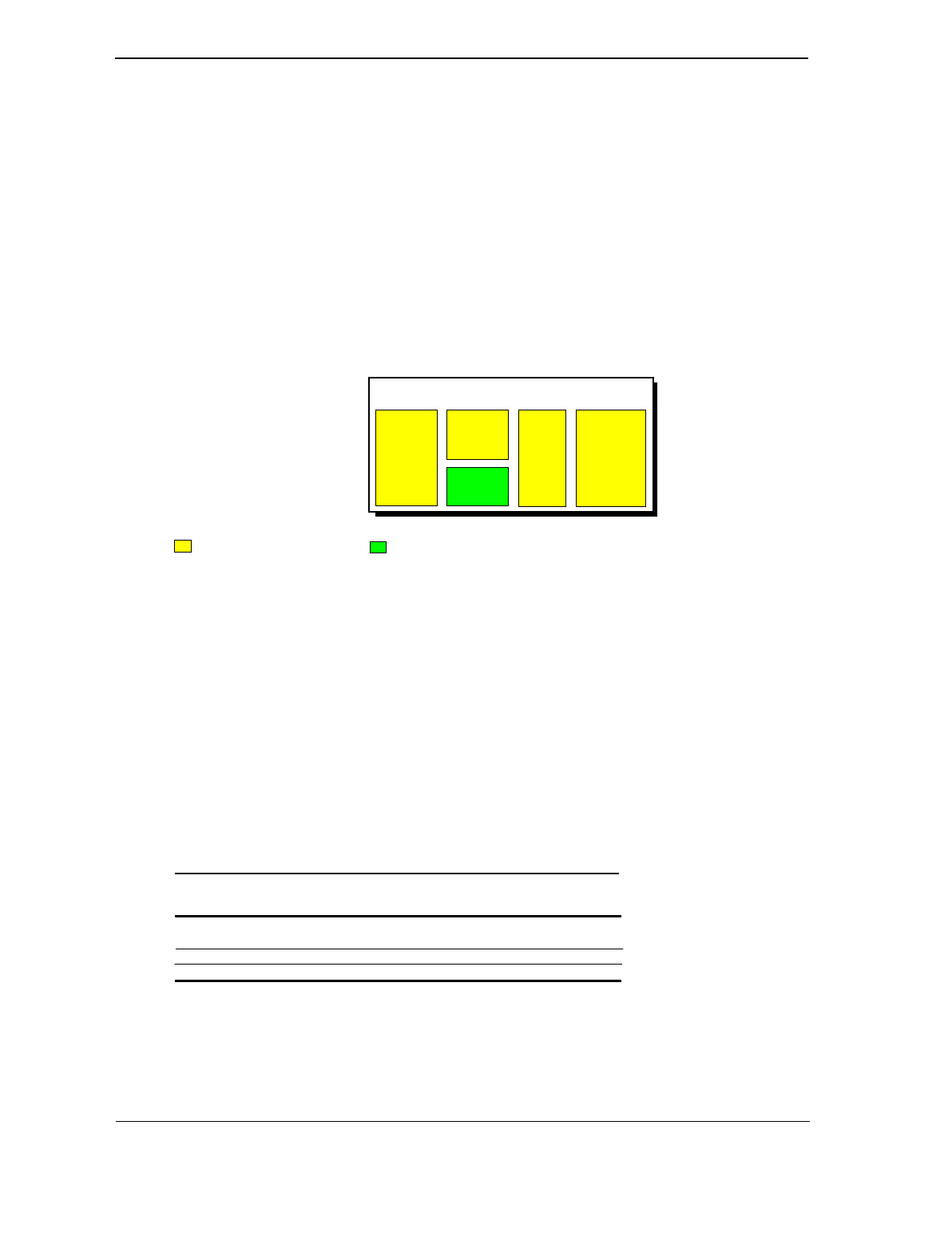
The Celeron processor (Figure 3-2) uses a dual-ALU CPU with branch prediction and MMX
support, floating point unit (FPU) for math coprocessing, a 32-KB primary (L1) cache, and a
128-KB secondary (L2) cache. All internal functions, except for the front side bus interface (FSB
I/F), operate at processor speed.
Figure 3–2.
Celeron Processor Internal Architecture
The Celeron processor is software-compatible with earlier generation Pentium II, Pentium MMX,
Pentium, and x86 processors. The MMX support provided by the Celeron consists of 57 special
instructions for accelerating multimedia communications applications. Such applications often
involve computing-intensive loops that can take up as much as 90 percent of the CPU’s execution
time. Using a parallel-processing technique called single-instruction multiple-data (SIMD),
MMX logic processes data 64 bits at a time. Specific applications that can benefit from MMX
technology include 2D/3D graphics, audio, speech recognition, video codecs, and data
compression.
The Celeron-based systems ship with a Celeron 500 installed. The 82810-DC100 GMCH
supports the processors listed in the following table:
Table 3–1.
Celeron Processor Statistical Comparison
Table 3-1.
Celeron Processor Statistical Comparison
Processor
Core/L1/L2
Freq.
FSB
Freq.
Core
Voltage
Power
Consumption
Celeron 500 500 MHz 66 MHz 2.0 v Na
Celeron 533 533 MHz 66 MHz 2.0 v Na
Celeron Processor
CPU
FPU
32-KB
L1
Cache
128-KB
L2
Cache
FSB
I/F
Core processin
g
speed Host bus speed


















