Overview of Monitoring and Recovery
HP Integrity NonStop NS-Series Operations Guide—529869-005
3-14
Determining Device States
The general format of the STATUS display follows. However, the format varies
depending on the subsystem.
where:
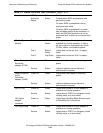
SCF Object States
Table 3-3 lists and explains the possible object states that the SCF STATUS command
can report.
subsystem STATUS object-type object-name
Name State PPID BPID attr1 attr2 attr3 …
object-name1 state nn,nnn nn,nnn val1 val2 val3 …
object-name2 state nn,nnn nn,nnn val1 val2 val3 …
subsystem The reporting subsystem name
object-type The object, or device, type
object-name The fully qualified name of the object
State One of the valid object states: ABORTING, DEFINED,
DIAGNOSING, INITIALIZED, SERVICING, STARTED, START-
ING, STOPPED, STOPPING, SUSPENDED, SUSPENDING, and
UNKNOWN
PPID The primary processor number and process identification number
(PIN) of the object
BPID The backup processor number and PIN of the object
attrn The name of an attribute of the object
valn The value of that object attribute
Table 3-3. SCF Object States (page 1 of 2)
State Substate Explanation
ABORTING The object is being aborted. The object is
responding to an ABORT command or some type
of malfunction. In this state, no new links are
allowed, and drastic measures might be underway
to reach the STOPPED state. This state is
irrevocable.
DEFINED One of the generally defined possible conditions of
an object with respect to the management of that
object.
DIAGNOSING The object is in a subsystem-defined test mode
entered through the DIAGNOSE command.
INITIALIZED The system has created the process, but it is not
yet in one of the operational states.