2.4 Special Paper
2-9
2.4 Special Paper
Besides plain paper, this printer can use the following types
of special paper:
Note
When printing on A4 size paper with thickness
above 200g/m
2
, feed the paper sideways from
the MP tray. Landscape feeding can cause
paper jams.
You can assign one of these special paper type to a paper
cassette or MP (multi-purpose) tray by using the printer’s
operator panel keys. Then, the printer can automatically
select the paper cassette or multi-purpose tray to feed the
special paper from and internally adjust the electrical
parameters for optimum printing performance according to
the special paper type. For details, see 3.10.4 Setting the
Cassette Paper Type on page 3-50.
Note that some types of special paper do not allow feeding
from the paper feeder cassette or duplex (two-sided) printing.
2.4.1 Selecting the special paper
Since special paper differs significantly in paper composition
and quality, special paper is more likely to cause problems
than white bond paper during printing. When using special
paper, be sure that they are manufactured for photocopiers
and/or printers.
Note
Kyocera Mita shall not be liable for any danger
to a person or machine that is caused by using
special paper (e.g., fumes emitted from the
special paper).
Before purchasing any special paper, make a test print using
the printer and check whether the results are satisfactory.
To avoid problems, stack transparencies, labels, or envelopes
on the tray or cassette face up.
Major considerations for each type of special paper are given
below.
Transparency
Transparencies for overhead projectors must withstand the
heat of fusing during the printing process. The recommended
transparency product is as follows:
3M CG3700 (Letter, A4)
To avoid problems, always feed OHP transparencies from the
Multi-purpose tray and output them to the optional Face Up
Tray.
When unloading transparencies (e.g., for clearing jams), hold
them carefully by the edges to avoid leaving fingerprints on
them.
Adhesive-backed labels
Label paper must be fed manually.
For printing on labels, use extreme care so that the adhesive
may not come in direct contact with any part of the printer.
Adhesives that stick to the drum or rollers will cause printer
damage.
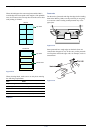
Labels consist of three parts. Printing is done onto the top
sheet (also called the face sheet). The adhesive contains
chemicals. The carrier sheet (also called the backing paper or
liner) bears the top sheet. This composition of labels can
cause more problems than other print forms during printing.
Figure 2-11
When using label paper, do not leave gaps between the
arranged labels (i.e., top sheets). Labels arranged with gaps
in-between can easily be peeled off during printing, causing
serious jam problems.
Paper type to be used Media type to be selected
Thin paper (60 to 64 g/m²) Vellum
Thick paper (105 to 220 g/m²) Thick
Overhead projector transparencies
Transparency
Postcards Cardstock
Envelopes Envelope
Labels Labels
Recycled paper Recycle
Colored paper Color
Preprinted paper Preprint
Table 2-4
Top sheet (white bond paper)
Adhesive
Carrier sheet