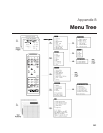
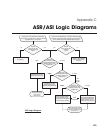
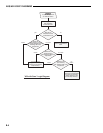
Resolution of ➤
the Projector
The smaller of CRT and Lens resolutions.
Retrace Time ➤
(Horizontal)
The minimum time required for the projector to move the position of the
scanning spot from the right edge to the left edge of a CRT.
Rise Time ➤ The time required by the video amplifier of the projector to increase its
output from 10% to 90% of the maximum value.
RGB Video ➤ The video output of most computers. It can be analog or digital. Analog
RGB video has 3, 4, or 5 wires; one for red, one for green, one for blue,
and none, one or two for sync. For three wire RGB, the green wire usually
provides sync. (See also TTL Video).
Scan Frequency ➤ The horizontal or vertical frequency at which images are generated.
Scan Line ➤ One scan line is one horizontal line on the display.
SECAM ➤ A video output format of some video tape and disk players (used primarily
in France). SECAM (Sequential Couleur á Mémoire) signals are similar in
resolution and frequency to PAL signals. The primary difference between
the two standards is in the way color information is encoded.
Setup Memory ➤ A projector memory which stores user-adjustable display settings. There are
two types of setup memories: Input and Recall. Both memory types store the
same parameters. The only difference is that Input memories store display
settings for a particular physical input (i.e., switcher 0, slot 1) and Recall
memories can be used with any input.
Slidebar ➤ A slidebar is a graphical display of an adjustment setting. The setting is
displayed on a percentage scale.
Source ➤ A device, such as a computer or VCR, which may be connected to the
projector for display.
Spot Size ➤ The diameter of the smallest dot that can be generated on the face of
a CRT.
GLOSSARY
A.7