MaxNAS Owner’s Manual
59
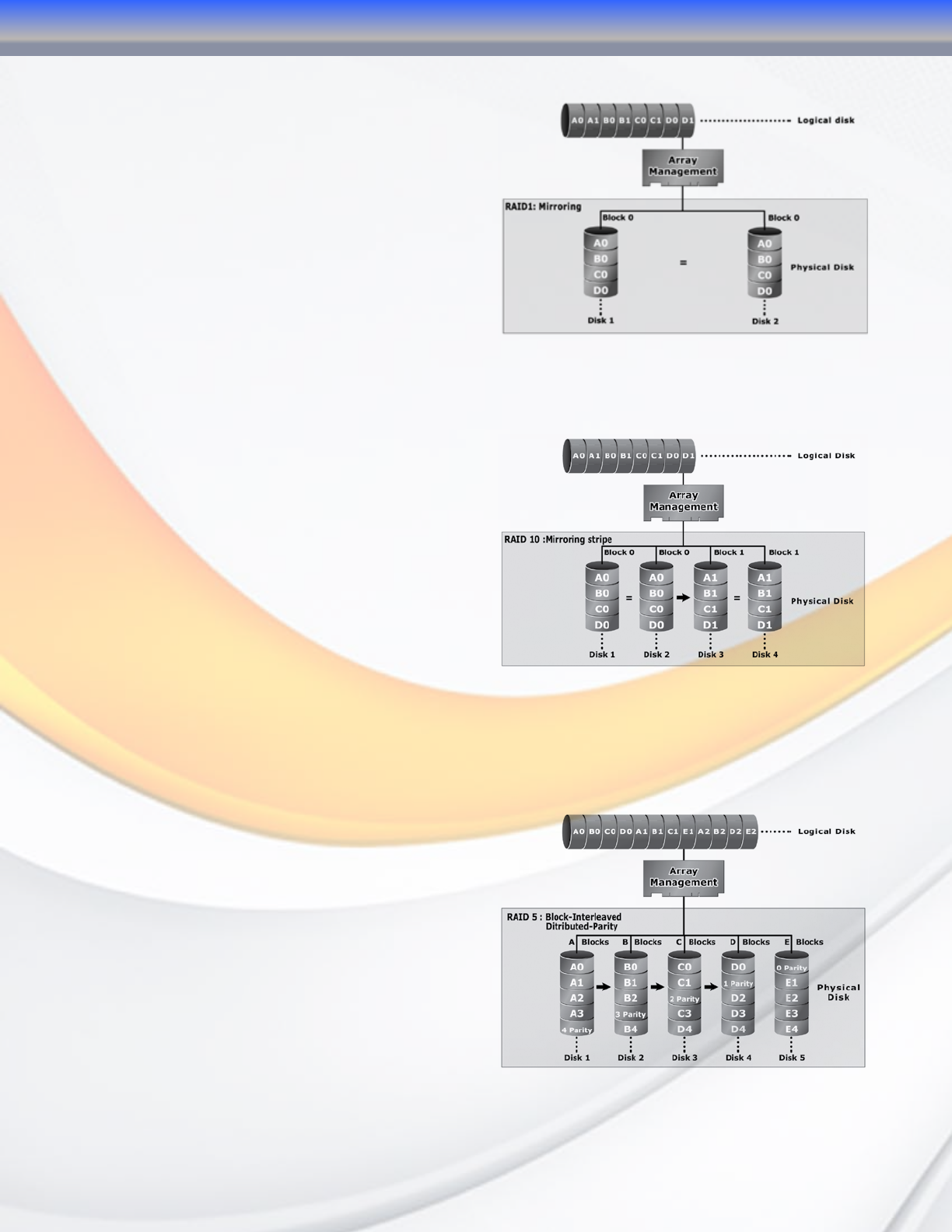
RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring)
RAID 1, also known as “disk mirroring”,
distributes duplicate data simultaneously to
pairs of disk drives.
Pros: RAID 1 offers extremely high data reliability
as all the data is redundant. If one drive
fails, all data (and software applications)
are preserved on the other drive.
Read performance may be enhanced as the
array controller can access both members
of a mirrored pair in parallel.
Cons: RAID 1 volume requires double the raw data storage capacity
Performance penalty when compared to writing to a single disk.
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID
1, combing striping with disk mirroring. RAID
Level 10 combines the fast performance of
Level 0 with the data redundancy of Leve1 1.
In this configuration, data is distributed across
several disk drives, similar to Level 0, which are
then duplicated to another set of drive for data
protection. RAID 10 provides the highest read/
write performance of any of the Hybrid RAID
levels, but at the cost of doubling the required
data storage capacity.
Pros: Fastest read/write performance of any of the Hybrid RAID levels
High data reliability as all the data is redundant
Cons: Requires double the raw data storage capacity
RAID 5
RAID 5 is sometimes called striping with parity
at byte level. In RAID 5, the parity information
is written to all of the drives in the subsystems
rather than concentrated on a dedicated parity
disk. If one drive in the system fails, the parity
information can be used to reconstruct the data
from that drive. All drives in the array system
can be used to seek operation at the same time,
greatly increasing the performance of the RAID
system. RAID 5 is the most often implemented
RAID algorithm in RAID arrays.
Pros: Very good general transfer performance
Fault tolerant
Cons: Can be slow at large size file transfers
5-Understanding RAID