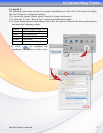
MaxNAS Owner’s Manual
65
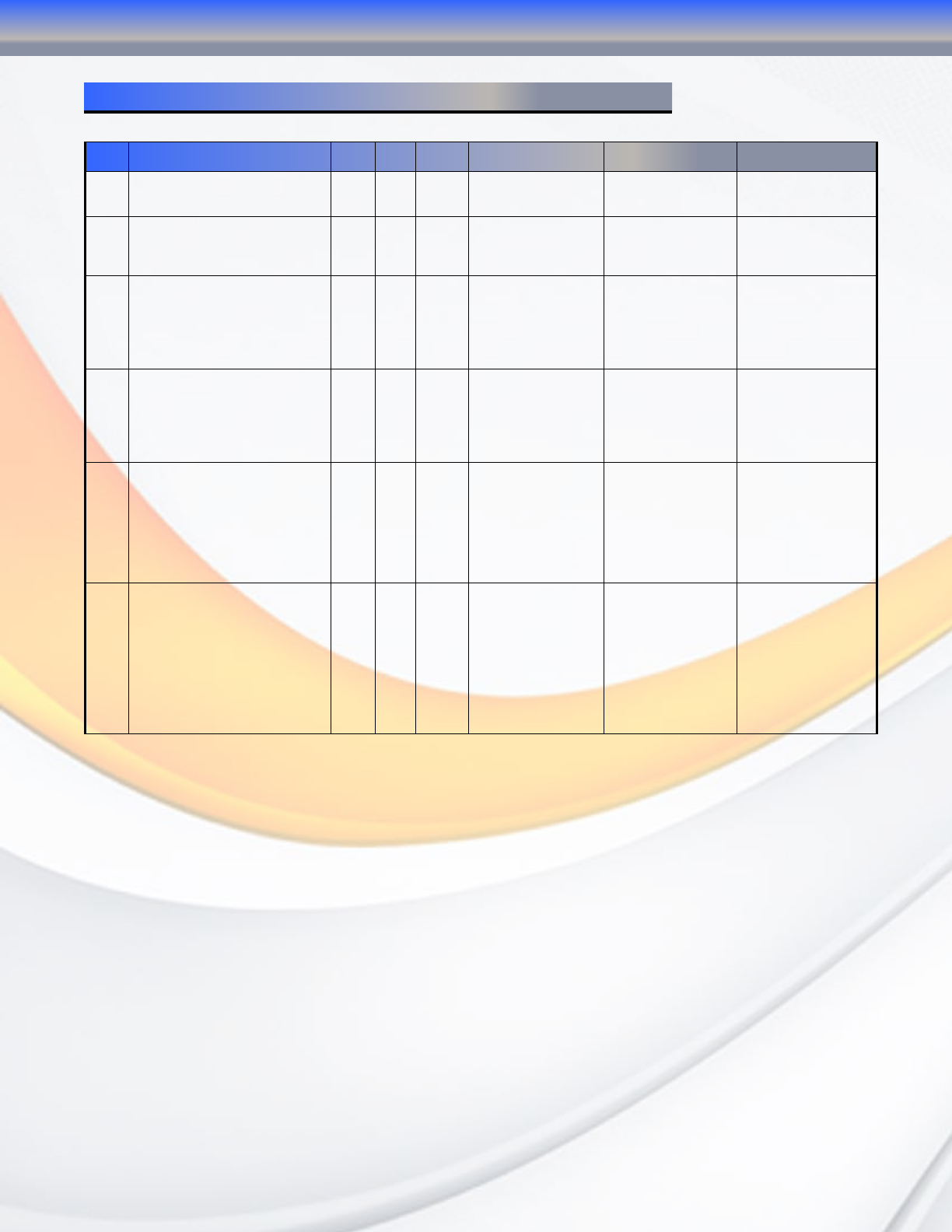
Appendix B: RAID Level Comparison Table
RAID
Level
Description Min.
Drives
Max.
Drives
Capacity Data
Reliability
Data
Transfer Rate
I/O
Request Rates
Span Also known as disk spanning. Data
is distributed sequentially to all
drives. There is no data protection.
1 4 (N)
Disks
No data protection Same as a single disk same as a single disk
0 Also known as striping
Data distributed across multiple
drives in the array simultaneously.
There is no data protection
1 4 (N)
Disks
No data
Protection
Very High Very High for
Both Reads and Writes
1 Also known as mirroring
All data replicated on N Separated
disks. N is always a multiple of 2.
This is a high availability Solution,
but due to the 100% data duplication,
it is also a costly solution.
2 4 1/(N )
Disks
Lower than RAID 6,
Higher than RAID 5
Reads are higher
Than a single disk;
Writes similar to a sin-
gle disk
Reads are twice faster
than a single disk;
Write are similar to a
single disk.
10 Also known as striped mirroring. Data
and parity information is subdivided
and distributed across all disks. This
is a high availability Solution, but
due to the 100% data duplication, it
is also a costly solution.
4 4 1/2 (N)
Disks
Lower than RAID 6,
higher than RAID 5
Reads are similar to
RAID 0
Writes are similar to
single disk
Reads are similar to
RAID 0
Writes are similar to sin-
gle disk
5 Also known Block-Interleaved
distributed Parity. Data and parity
information is subdivided and
distributed across all disk. Parity
must be the equal to the smallest
disk capacity in the array. Parity
information normally stored on a
dedicated parity disk.
3 5 (N-1)
Disks
Lower than RAID 1, 10
Higher than a single
drive
Reads are similar to
RAID 0;
Writes are slower than
RAID 0
Reads are similar to
RAID 0;
Writes are slower than a
single disk.
6 Also known as dual parity. Similar
to RAID 5, but does two different
parity computations or the same
computation on overlapping subsets
of the data. The RAID 6 can offer
fault tolerance greater that RAID
1 or RAID 5 but only consumes
the capacity of 2 disk drives for
distributed parity data reliability
similar to RAID 0.
4 5 (N-2
Disks)
Highest Reliability Reads are similar to
RAID 0;
Writes are slower than
RAID 5
Reads are similar to
RAID 0;
Writes are slower than a
single disk.
B-RAID Level Comparison Table