Chapter 6: Using the Software
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. 108
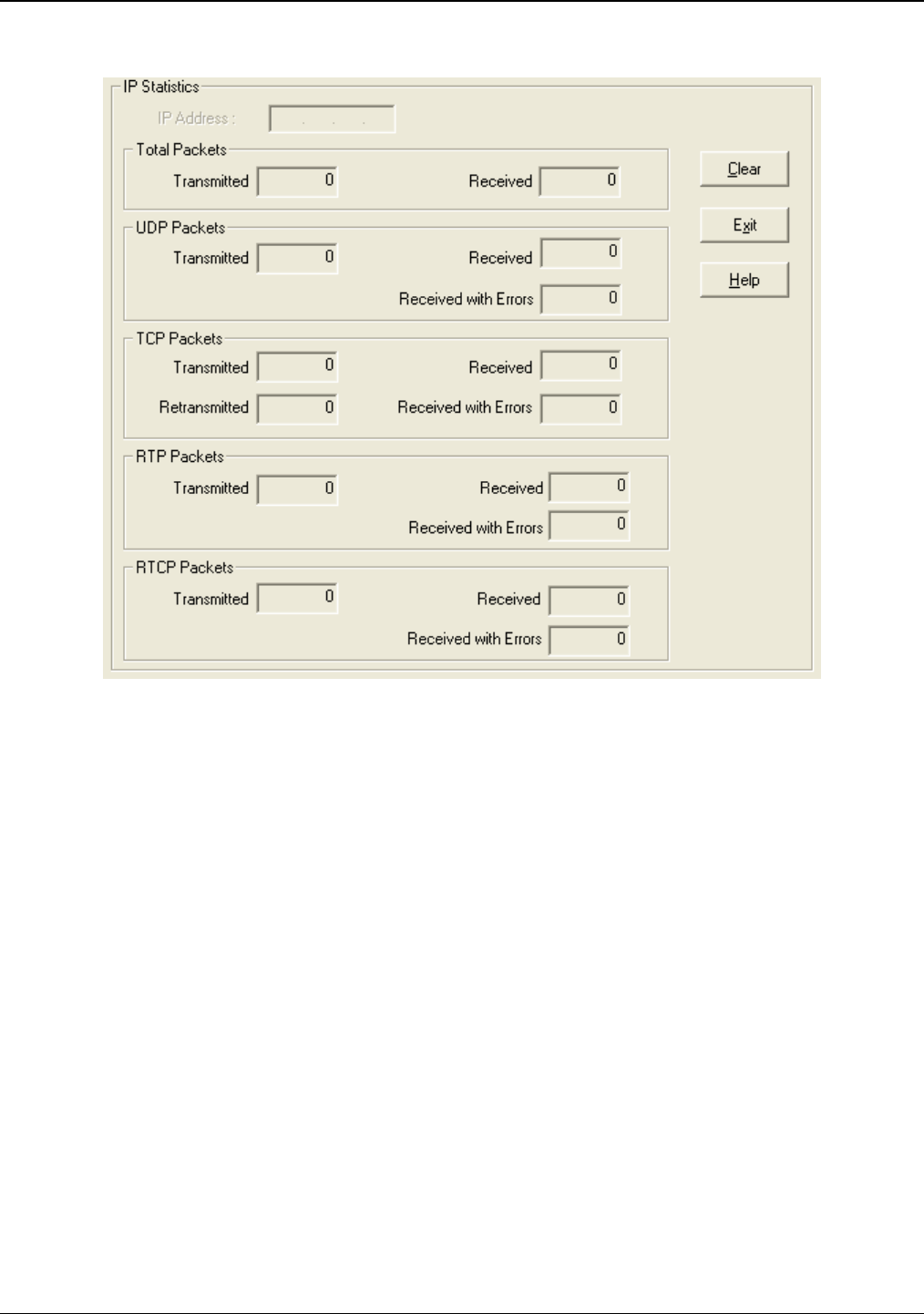
IP Statistics
Figure 6-5: IP statistics screen
UDP versus TCP. (User Datagram Protocol versus Transmission Control Protocol). UDP provides
unguaranteed, connectionless transmission of data across an IP network. By contrast, TCP provides reliable,
connection-oriented transmission of data.
Both TCP and UDP split data into packets called “datagrams.” However, TCP includes extra headers in the
datagram to enable retransmission of lost packets and reassembly of packets into their correct order if they arrive
out of order. UDP does not provide this. Lost UDP packets are irretrievable; that is, out-of-order UDP packets
cannot be reconstituted in their proper order.
Despite these obvious disadvantages, UDP packets can be transmitted much faster than TCP packets -- as much
as three times faster. In certain applications, like audio and video data transmission, the need for high speed
outweighs the need for verified data integrity. Sound or pictures often remain intelligible despite a certain amount
of lost or disordered data packets (which comes through as static).