Chapter 5: Phonebook Configuration
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. 85
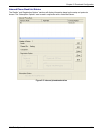
Clicking on the Advanced button brings up the Alternate Routing secondary screen. This feature provides an
alternate path for calls if the primary IP network cannot carry the traffic. Often in cases of failure, call traffic is
temporarily diverted into the PSTN. However, this feature could also be used to divert traffic to a redundant
(backup) unit in case one VOIP unit fails. The user must specify the IP address of the alternate route for each
destination pattern entry in the Outbound Phonebook.
Figure 5-3: Advanced button
Alternate Routing Field Definitions
Field Name
V
alues Description
Alternate IP
Address
n.n.n.n
Alternate destination for outbound data traffic in case of excessive delay in data
transmission.
Round Trip
Delay
Default is
300
milliseconds
The Round Trip Delay is the criterion for judging when a data pathway is
considered blocked. When the delay exceeds the threshold specified here, the
data stream will be diverted to the alternate destination specified as the Alternate IP
Address.
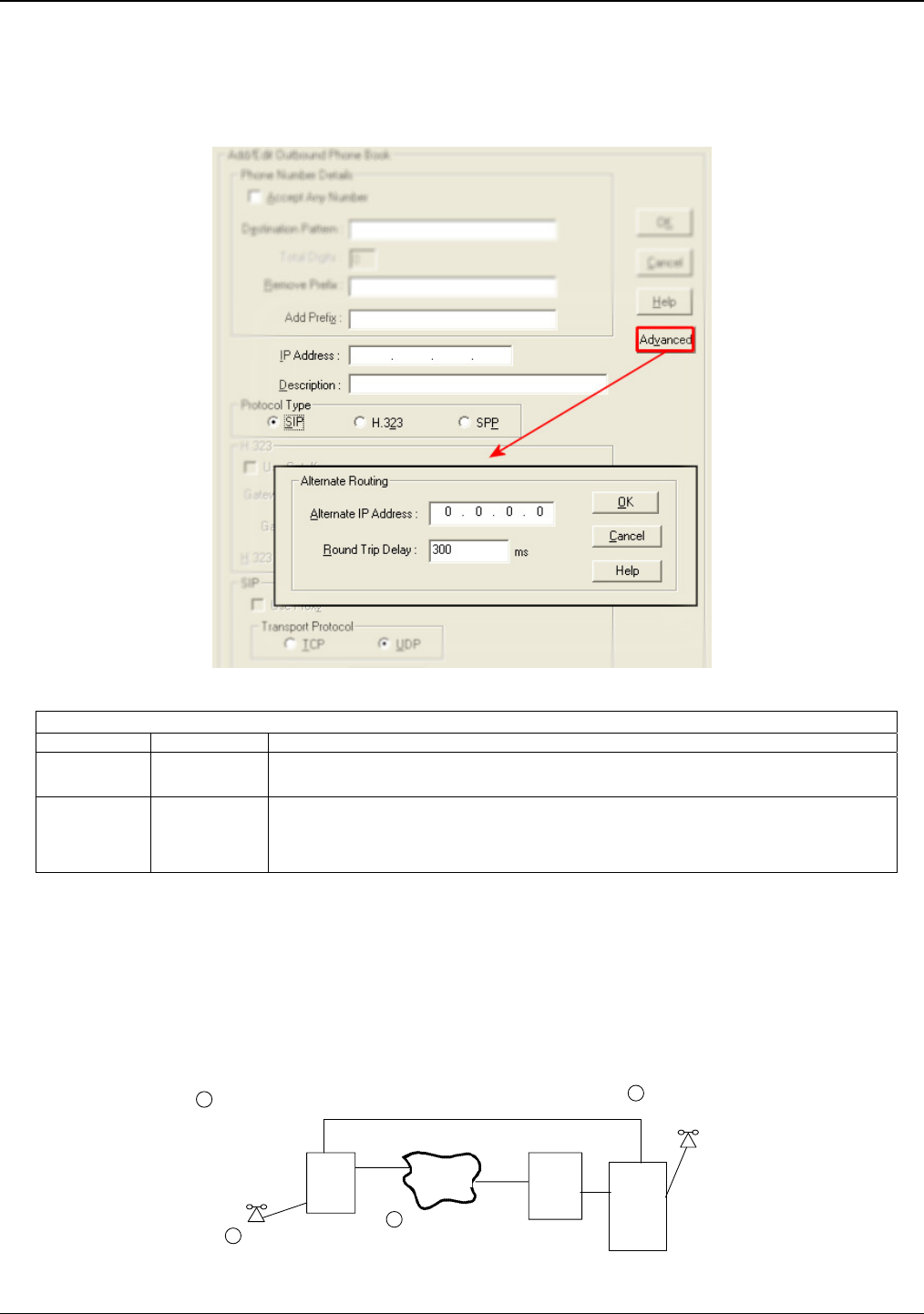
The Alternate Routing function facilitates PSTN Failover protection, that is, it allows you to re-route VOIP calls
automatically over the PSTN if the VOIP system fails. The MultiVOIP can be programmed to respond to excessive
delays in the transmission of voice packets, which the MultiVOIP interprets as a failure of the IP network. Upon
detecting an excessive delay in transmission of voice packets (overly high “latency” in the network) the MultiVOIP
diverts the call to another IP address, which itself is connected to the PSTN (for example, via an FXO port on the
self-same MultiVOIP could be connected to the PSTN).
PSTN Failover Feature. The MultiVOIP can be programmed to divert calls to the PSTN temporarily in case the IP
network fails. See Figure 5-4 below for example.
IP
NETWORK
FXS
FXO
VOIP
VOIP
PBX
PSTN Line
1. Call originates.
2. IP network fails.
3. Call diverts to
Alt IP address in voip
accessing PSTN line.
4. Call completed
via PSTN.
Figure 5-4: PSTN failover