Glossary
GL-2
7610-A2-GB20-10
November 1997
Data Communications Equipment. The equipment that provides the functions required to
establish, maintain, and end a connection. It also provides the signal conversion required
for communication between the DTE and the network.
Digital Data Service. Provides digital communication circuits.
Data Mode Idle. Refers to a sequence of ones transmitted or received on the DDS
network.
Data Set Ready. An EIA-lead standard for V.24 circuit CT 107; an output signal
(DCE-to-DTE).
Data Service Unit. Data communications equipment that provides an interface between the
DTE and the digital network.
Data Terminal Equipment. The equipment, such as computers and printers, that provides
or creates data.
Data Terminal Ready. An EIA-lead standard for V.24 circuit CT 108; an input signal
(DTE-to-DCE).
Electronic Industries Association. This organization provides standards for the data
communications industry to ensure uniformity of interface between DTEs and DCEs.
The EIA’s standards defining the 25-pin interface between the DTE and DCE.
MIB objects unique to Paradyne devices.
An excessive bipolar violation condition results when at least one invalid bipolar violation
has occurred every 20 milliseconds for 2 seconds.
A predetermined set of configuration options for general operation.
Federal Communications Commission. Board of Commissioners that regulates all U.S.
interstate, intrastate, and foreign electrical communication systems that originate from the
United States.
A switching interface that is designed to get frames from one part of the network to another
as quickly as possible.
The capability to transmit in two directions simultaneously.
High-Level Data Link Control. A communications protocol defined by the International
Standards Organization (ISO).
Internet Control Management Protocol. Internet protocol that allows for the generation of
error messages, tests packets, and information messages related to IP.
In-band Management Channel. A proprietary TDM channel used for IP connectivity.
A shared boundary between functional units.
Internet Protocol. The TCP/IP standard protocol that defines the unit of information passed
across an Internet and provides the basis for packet delivery service. IP includes the ICMP
control and error message protocol as an integral part. The entire protocol suite is often
referred to as TCP/IP because TCP and IP are the two most fundamental protocols.
The IP address has a host component and a network component. The address is assigned
to hosts or workstations with direct Internet access to uniquely identify entities on the
Internet.
International Telecommunication Union, formerly known as CCITT. An advisory committee
established by the United Nations to recommend communications standards and policies.
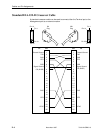
Local Area Data Set is used to provide a point-to-point link between two devices (also
called LDM – limited distance modem).
DCE
DDS
DMI
DSR
DSU
DTE
DTR
EIA
EIA-232
Enterprise MIB
excessive BPV
factory defaults
FCC
frame relay
full-duplex
HDLC
ICMP
IMC
interface
IP
IP address
ITU
LADS