2–Configuring NIC
NIC Partitioning (NPAR)
SN0054671-00 B 2-43
NPAR QoS allows NIC partitions to each allocate a minimum guaranteed portion
of the available bandwidth. QoS bandwidth only applies only to NIC partitions.
iSCSI partitions are not supported by the QoS bandwidth allocation. This brings
up the possibility that, if the total minimum allocated bandwidth across the NIC
partitions equals 100 percent, then the iSCSI partition will be limited to 1 percent
of the NIC bandwidth portion in high-utilization conditions.
To ensure that iSCSI has more than 1 percent of bandwidth available in
high-utilization conditions, set the total NPAR QoS minimum bandwidth settings
so that they equal less than 100 percent.
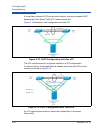
Example
An NPAR enabled port has two NIC partitions, one iSCSI partition, and one
FCoE partition.
ETS allocates 50 percent of the network bandwidth to FCoE traffic and
50 percent to non-FCoE traffic.
The NPAR QoS minimum bandwidth setting for each NIC partition is
50 percent.
This setting means that each NIC partition is guaranteed 50 percent of
50 percent of 10Gb, or 2.5Gb each.
If at any time the FCoE partition is using 5Gb of bandwidth and each NIC
partition is using 2.5Gb, then the iSCSI partition is left with only 50Mb of
bandwidth.
If, however, the NIC partitions each allocated 45 percent of the non-FCoE
traffic, then the total allocated bandwidth would be 90 percent.
The remaining 10 percent (or 500 Mb) would then be effectively
reserved for the iSCSi partition.
eSwitch
The 8200 and 3200 Series Adapters support embedded switch (eSwitch)
functionality, which provides a basic VLAN-aware Layer-2 switch for Ethernet
frames. Each physical port has one instance of an eSwitch, which supports all
NPARs on that physical port.
The eSwitch operation is transparent and the administrator does not need to
perform any specific configuration. The ability to view eSwitch statistics depends
on your operating environment and management tool.
The QLogic drivers download the VM MAC addresses to the firmware, which
enables the firmware and hardware to switch the packets destined for VMs on the
host.
For traffic to flow from one eSwitch to another, it must first pass through an
external switch or have been forwarded by a VM that has a path through both
eSwitches.