Si53xx-RM
Rev. 0.5 69
At power-on or reset, the valid CKINn with the highest priority (1 being the highest priority) is automatically
selected. If no valid CKINn is available, the device suppresses the output clocks and waits for a valid CKINn signal.
If the currently selected CKINn goes into an alarm state, the next valid CKINn in priority order is selected. If no valid
CKINn is available, the device enters Digital Hold.
Operation in revertive and non- revertive is different when a signal becomes valid:
Revertive (AUTOSEL = H): The device constantly monitors all CKINn. If a CKINn with a higher priority than
the current active CKINn becomes valid, the active CKINn is changed to the
CKINn with the highest priority.
Non-revertive (AUTOSEL = M): The active clock does not change until there is an alarm on the active clock. The
device will then select the highest priority CKINn that is valid. Once in digital hold,
the device will switch to the first CKINn that becomes valid.
6.3.3. Hitless Switching with Phase Build-Out (Si5323, Si5366)
Silicon Laboratories switching technology performs “phase build-out” to minimize the propagation of phase
transients to the clock outputs during input clock switching. All switching between input clocks occurs within the
input multiplexor and phase detector circuitry. The phase detector circuitry continually monitors the phase
difference between each input clock and the DSPLL output clock, f
OSC
. The phase detector circuitry can lock to a
clock signal at a specified phase offset relative to f
OSC
so that the phase offset is maintained by the PLL circuitry.
At the time a clock switch occurs, the phase detector circuitry knows both the input-to-output phase relationship for
the original input clock and for the new input clock. The phase detector circuitry locks to the new input clock at the
new clock's phase offset so that the phase of the output clock is not disturbed. The phase difference between the
two input clocks is absorbed in the phase detector's offset value, rather than being propagated to the clock output.
The switching technology virtually eliminates the output clock phase transients traditionally associated with clock
rearrangement (input clock switching).
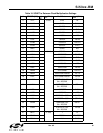
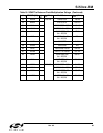
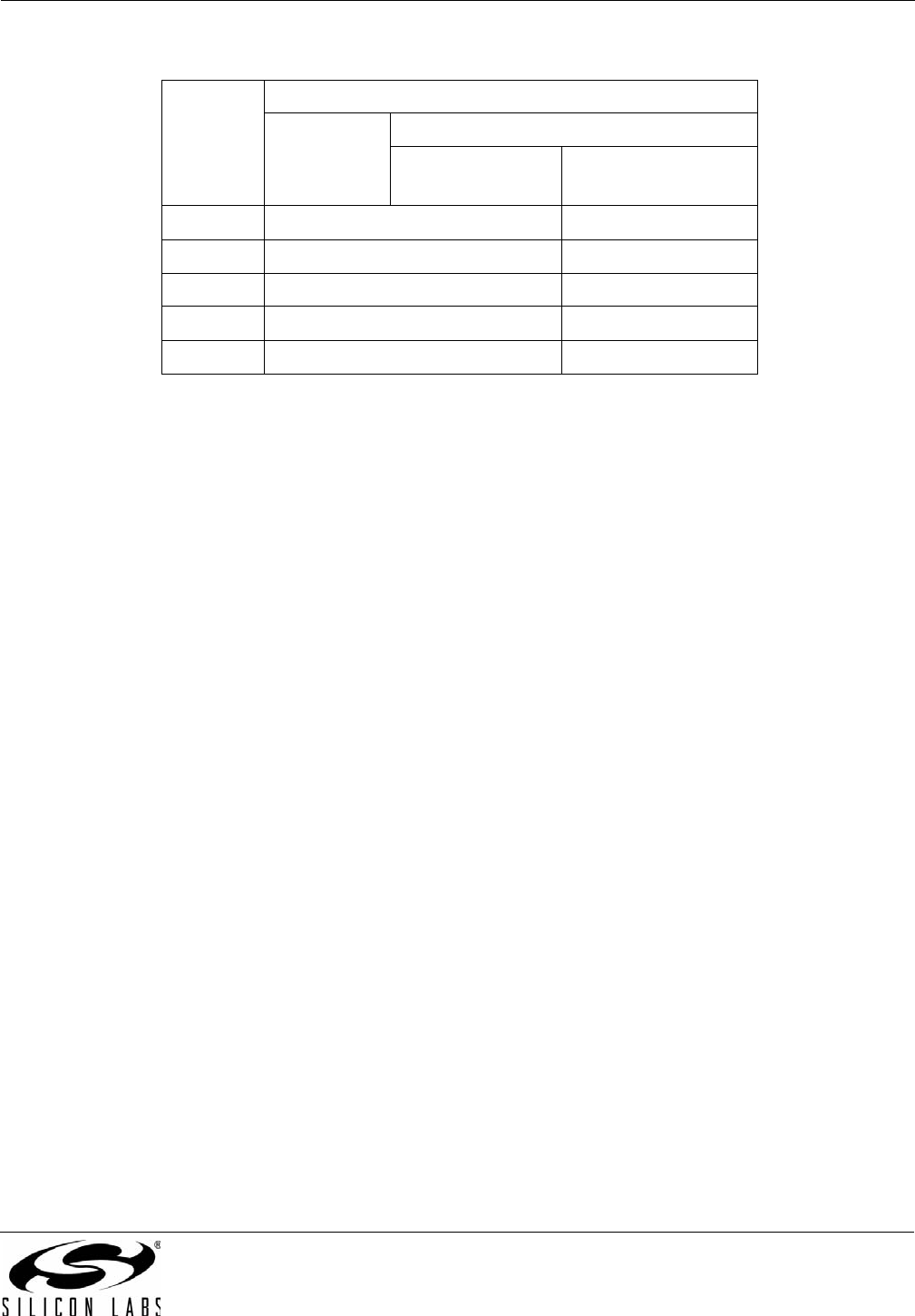
Table 28. Input Clock Priority for Auto Switching (Si5365, Si5366)
Priority Input Clock Configuration
Si5365 Si5366
4 Input Clocks
(CK_CONF = 0)
FSYNC Switching
(CK_CONF = 1)
1 CKIN1 CKIN1/CKIN3
2 CKIN2 CKIN2/CKIN4
3 CKIN3 N/A
4 CKIN4 N/A
5 Digital Hold Digital Hold