Xerox
®
DocuMate
®
4830
User’s Guide
168
Threshold and Dynamic threshold
Threshold enables you to set what level of light or dark to look for on a page. When scanning in black and white,
everything on the page is set to either white pixels or black pixels in the final image. If the text on the page is a light
color, then the text may be gone in the final image as the scanner will change those light colors to white pixels. The
threshold slider lets you set the level of darkness or lightness of the text on the page. Dynamic threshold attempts
to evaluate the image and dynamically adjust the threshold level. These options work best for documents that
contain only text such as business letters, spreadsheets, reports, etc...
• Threshold—move the slider to the left or right to set the level of lightness or darkness for the scanner to
leverage from.
For example, if you are scanning a document with gray text, such as hand written pencil notes, move the slider
to the right. This tells the scanner that the level to look for is light, and gray pixels are converted to black pixels
instead of white. If the overall tone of the original document is dark, such as a colored background that may
interfere with detecting black, move the slider left. This tells the scanner that the level to look for is dark, only
very dark areas such as text are converted to black pixels.
If you are scanning documents that are in good condition, with black text on a white background, the default
threshold option will properly scan the item. This level only needs to be adjusted if the scanned image does not
have image clarity similar to the original.
• Sensitivity—move the slider left or right to adjust the sensitivity level for dynamic thresholding. This slider is
only enabled when Dynamic threshold is selected in the list.
Error diffusion, Bayer, and Halftone pattern
Error diffusion, Bayer, and Halftone patterns are the intentional application of noise (dithering) in the image to
help alleviate banding when scanning in binary (black and white) mode. For example, if you scan a color photo in
black and white, the image file will have large blocks of black and white and the image barely recognizable.
Dithering the image creates a black and white image that is recognizable.
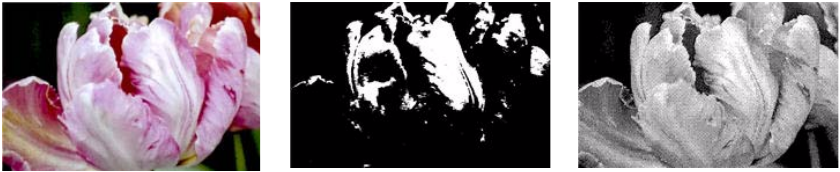
Below is an example of a color scan, a black and white scan without dithering, and a black and white scan with
dithering. When the image is scaled down, it may look like a grayscale scan. When the image is at normal size or
enlarged you will be able to clearly see the dithering pattern, as shown in the close-up image.
Color scan
Black and White scan Bayer dither scan