ES-2024 Series User’s Guide
159
CHAPTER 21
IP Source Guard
Use IP source guard to filter unauthorized ARP packets in your network.
21.1 IP Source Guard Overview
IP source guard uses a binding table to distinguish between authorized and unauthorized ARP
packets in your network. A binding contains these key attributes:
• MAC address
• VLAN ID
• IP address
• Port number
When the Switch receives an ARP packet, it looks up the appropriate MAC address, VLAN
ID, IP address, and port number in the binding table. If there is a binding, the Switch forwards
the packet. If there is not a binding, the Switch discards the packet.
The Switch builds from information provided manually by administrators (static bindings).
IP source guard consists of the following features:
• Static bindings. Use this to create static bindings in the binding table.
• ARP inspection. Use this to filter unauthorized ARP packets on the network.
21.1.1 ARP Inspection Overview
Use ARP inspection to filter unauthorized ARP packets on the network. This can prevent
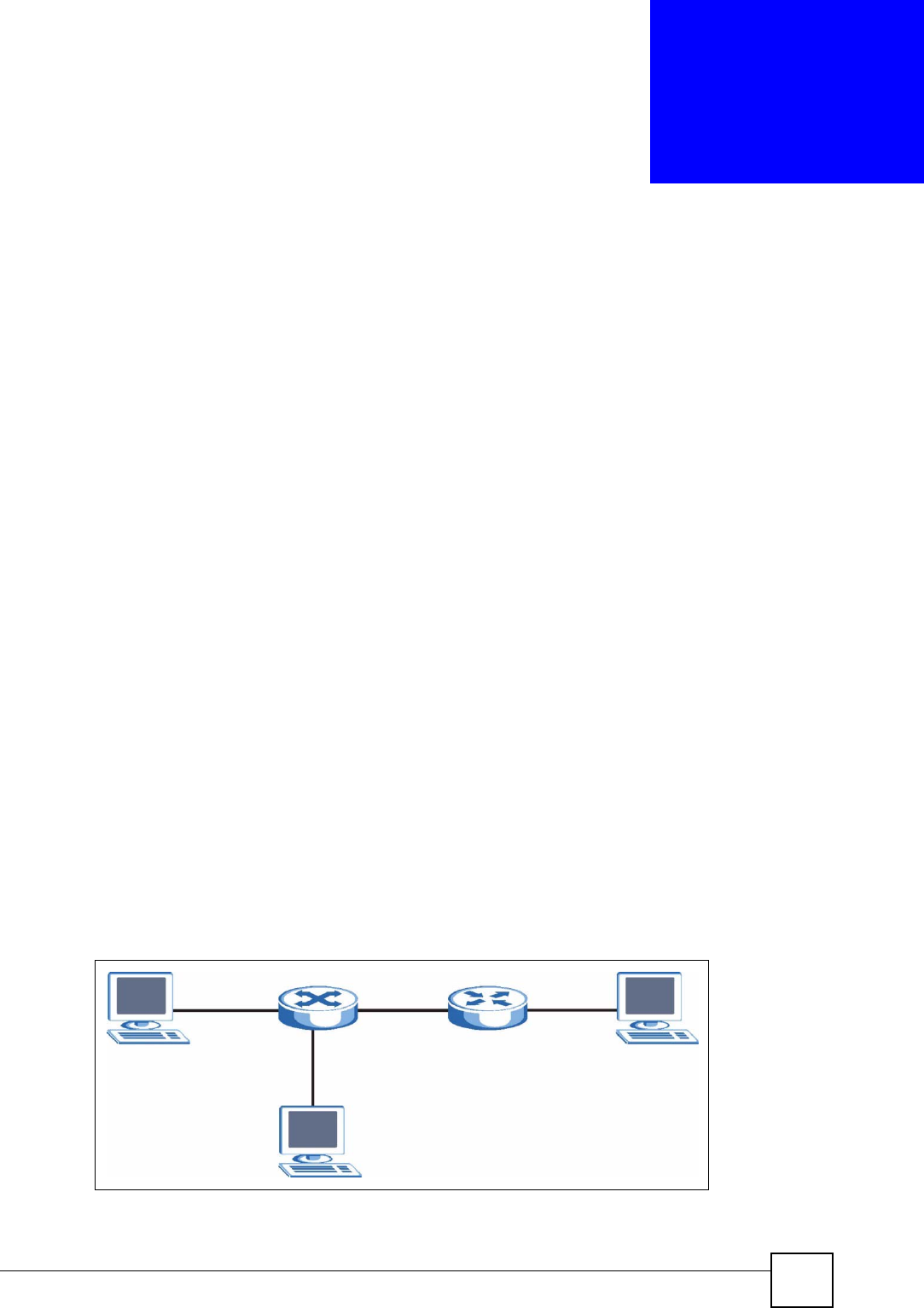
many kinds of man-in-the-middle attacks, such as the one in the following example.
Figure 80 Example: Man-in-the-middle Attack
A
X
B


















