297
EES4710BD 10 Slots L2/L3/L4 Chassis Switch
Chapter 14 DHCP Configuration
14.1 Introduction to DHCP
DHCP [RFC2131] is the acronym for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is a protocol that
assigns dynamically IP addresses to request host from the address pool as well as other network
configuration parameters such as default gateway, DNS server, default route and host image file
position within the network. DHCP is the enhanced version of BootP. It is a mainstream technology
that can not only provide boot information for diskless workstations, but can also release the
administrators from manual recording IP allocation and reduce user effort and configuration.
Another benefit of DHCP is it can partially ease the pressure on IP demands, when the user of an IP
leaves the network, their IP can be assigned to another user.
DHCP is a client-server protocol, the DHCP client requests the network address and configuration
parameters from the DHCP server; the server provides the network address and configuration
parameters for the clients; if a DHCP server and clients are located in different subnets, DHCP relay
is required for DHCP packets to be transferred between the them. The implementation of DHCP is
shown below:
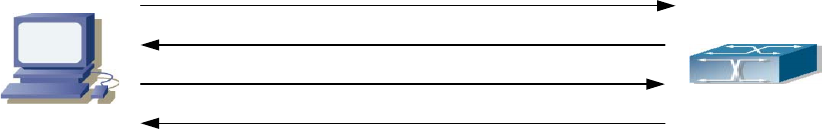
Fig 14-1 DHCP protocol interaction
Explanation:
1. DHCP client broadcasts DHCPDISCOVER packets in the local subnet.
2. On receiving the DHCPDISCOVER packet, DHCP server sends a DHCPOFFER packet along
with IP address and other network parameters to the DHCP client.
3. DHCP client broadcast DHCPREQUEST packet with the information for the DHCP server it
selected after selecting from the DHCPOFFER packets.
4. The DHCP server selected by the client sends a DHCPACK packet and the client gets an IP
address and other network configuration parameters.
The above four steps finish a Dynamic host configuration assignment process. However, if the
DHCP server and the DHCP client are not in the same network, the server will not receive the
DHCP broadcast packets sent by the client, therefore no DHCP packets will be sent to the client by
the server. In this case, a DHCP relay is required to forward such DHCP packets so that the DHCP
packets exchange can be completed between the DHCP client and server.
ES4710BD can act as both a DHCP server and a DHCP relay. DHCP server supports not only
dynamic IP address assignment, but also manual IP address binding (i.e., specify a specific IP
address to a specified MAC address or specified device ID over a long period. The differences and
relations between dynamic IP address allocation and manual IP address binding are: 1) IP address


















